Craniopharyngiomas are rare intracranial dysontogenic tumors with benign histology and malignant behavior
What is the Pathology of Craniopharyngiomas?
The pathology of craniopharyngiomas is:
-Etiology: The cause of craniopharyngiomas is fragments of the Rathke cleft and craniopharyngeal duct and gene mutation and involvement.
-Genes involved: Beta-catenin gene, BRAF (V600E).
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to craniopharyngiomas; arise from the proliferation of epithelial-squamous cells lining the pituitary stalk.
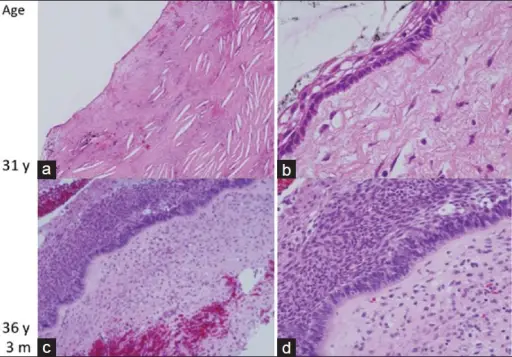
-Morphology: The morphology associated with craniopharyngiomas shows large cysts or multiple cysts with solid components, fibrous tissue necrotic debris, and calcifications.
-Histology: The histology associated with craniopharyngiomas shows the basal layer of trivial cells, darkly stained nuclei and slight cytoplasm, keratinized to flat plate-like squamous cells.
How does Craniopharyngiomas Present?
Patients with craniopharyngiomas typically has no gender prevalence, present at age range of 5 to 65 years The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with craniopharyngiomas include endocrine dysfunction, headache visual disturbances, cold intolerance, weight gain, excessive fatigue, adrenal failure symptoms diabetes insipidus and reduced sexual drive.
How are Craniopharyngiomas Diagnosed?
Craniopharyngiomas are diagnosed through laboratory studies, complete endocrine evaluation (serum and urine osmolality thyroid functioning tests, growth hormone levels).
How is Craniopharyngiomas Treated?
Craniopharyngiomas are treated through surgical resection, radiation therapy, or chemotherapy.
What is the Prognosis of Craniopharyngiomas?
The prognosis of craniopharyngiomas is good.