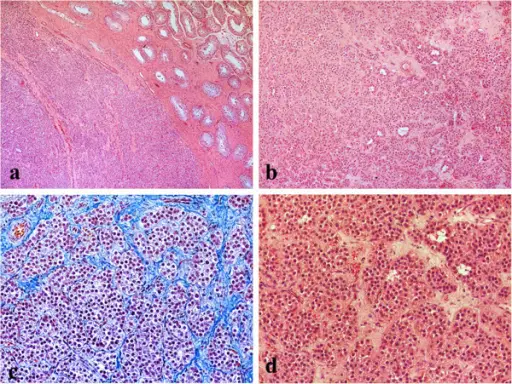
Leydig cell tumors of the testis. a. The tumor was surrounded by an incomplete, dense lamellar area. In non-neoplastic testicular tissue, the seminiferous tubules showed Sertoli cells with complete spermatogenesis, hematoxylin-eosin stain x10 b. No evidence of necrosis, or vascular invasion was seen. Stroma was fibrous with prominent vascularity, hematoxylin-eosin stain x10 c. The testicular tumor was composed of nests, insular or pseudotubular pattern, hematoxylin-eosin and methylene blue stain x40 d. The tumor cells were large, polygonal, with acidophilic to vacuolated cytoplasm and regular round nuclei, some with visible nucleoli. Mitoses were scarce, hematoxylin-eosin stain x40.Leydig cell tumors of the testis: a case report.
Gheorghisan-Galateanu AA - BMC research notes (2014). Not Altered. CC.
Testicular tumors are lesions of testis divided into two major classes: germ cell tumors and nongerminal tumors.
Examples of testicular tumors include:
- Testicular lymphoma
- Gonadoblastoma
- Tumors of sex cord-gonadal stroma
- Germ cell tumors
