Rhabdomyosarcoma is a mesenchymal aggressive malignant tumor of skeletal muscle differentiation. There are different types of rhabdomyosarcomas which include alveolar, embryonal, and pleomorphic.
What is the Pathology of Rhabdomyosarcoma?
The pathology of rhabdomyosarcoma is:
-Etiology: The cause of rhabdomyosarcoma is disruption of skeletal muscle progenitor cell growth and related differentiation.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to rhabdomyosarcoma is unclear.
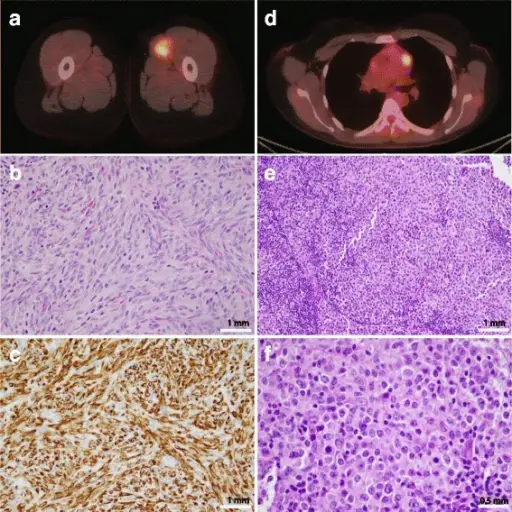
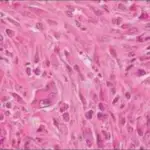
-Morphology: The morphology associated with rhabdomyosarcoma shows small, round tumor cells with hyperchromatic nuclei and large, polygonal-shaped tumor cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm, which often contains diagnostic cross striations.
-Histology: The histology associated with rhabdomyosarcoma shows sheets of small, round cells clustered with variable amounts of fibrous septa; may contain scattered giant cells (alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma.
How does Rhabdomyosarcoma Present?
Patients with rhabdomyosarcoma typically affect males present at the age range of 25 or less. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with rhabdomyosarcoma include a persistent lump or swelling in the part of the body, bulging of the eye or a swollen eyelid, headache and nausea, trouble urinating or having bowel movements, blood in the urine, bleeding from the nose, throat, vagina, or rectum.
How is Rhabdomyosarcoma Diagnosed?
Rhabdomyosarcoma is diagnosed using ultrasound imaging.
How is Rhabdomyosarcoma Treated?
Rhabdomyosarcoma is treated with wide excision without axillary dissection, adjuvant or neoadjuvant radiation.
What is the Prognosis of Rhabdomyosarcoma?
The prognosis of rhabdomyosarcoma is poor.