Leiomyoma is the bland smooth muscle tumor without mitotic figures.
What is the Pathology of Leiomyoma?
The pathology of leiomyoma is:
-Etiology: The cause of leiomyoma is ischemia or hormonal stimulation.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to leiomyoma is not well understood.
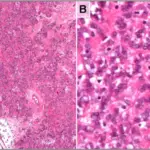
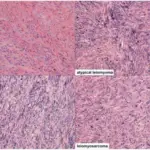
-Morphology: The morphology associated with leiomyoma shows monotonous spindle cells with indistinct borders arranged in intersecting fascicles.
-Histology: The histology associated with leiomyoma shows bundles or fascicles of spindled cells with eosinophilic and possibly fibrillary cytoplasm.
How does Leiomyoma Present?
Patients with leiomyoma typically affect women present in the age range of 40 and above (postmenopausal). The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with leiomyoma include menorrhagia, pelvic pain, pelvic pressure, frequent urination, heavy menstrual bleeding, and difficulty emptying the bladder.
How is Leiomyoma Diagnosed?
Leiomyoma is diagnosed using ultrasound and MRI.
How is Leiomyoma Treated?
Leiomyoma is treated with hysterectomy or myomectomy.
What is the Prognosis of Leiomyoma?
The prognosis of leiomyoma is excellent as the patient remains asymptomatic for many years or indefinitely.