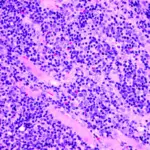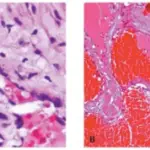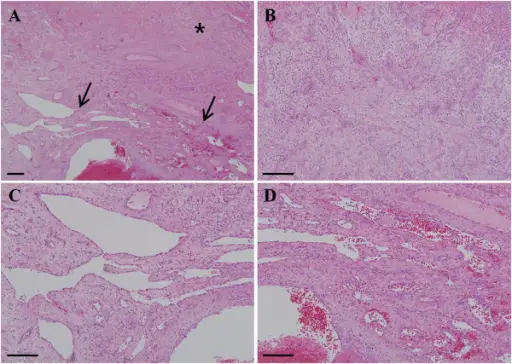
Hematoxylin and eosin staining features of specimen. (A) Tumor specimen at low magnification. Asterisk (*) indicates the pyogenic granuloma portion of the lesion, and arrows show the development of capillary hemangioma and thrombosis. (B) The pyogenic granuloma portion at higher magnification. Edematous granulation tissues and numerous small blood vessels with neutrophil infiltration were observed under the epithelium of the tumor. (C and D) Capillary hemangioma portion of the tumor at higher magnification showing numerous newly generated blood vessels filled with thrombi. Newly developed capillary vessels were seen to communicate with each other and lined with a thin endothelial cell layer. Scale bar = 200μm.Co-development of pyogenic granuloma and capillary hemangioma on the alveolar ridge associated with a dental implant: a case report.
Kang YH, Byun JH, Choi MJ, Lee JS, Jang JH, Kim YI, Park BW - Journal of medical case reports(2014). Not Altered. CC.
Capillary hemangiomas are an overgrowth of capillary blood vessels seen commonly in the skin.
What is the Pathology of Capillary Hemangiomas?
The pathology of capillary hemangiomas is abnormal proliferation of normal tissue in a normal position.
How do Capillary Hemangiomas Present?
Capillary hemangiomas present with cutaneous lesion, subcutaneous lesion, orbital lesion.
How are Capillary Hemangiomas Diagnosed?
Capillary hemangiomas are diagnosed by ultrasound, CT scan, and MRI.
How are Capillary Hemangiomas Treated?
Capillary hemangiomas are treated with beta-blocker, radiation therapy, surgical excision, laser photocoagulation.
What is the Prognosis of Capillary Hemangiomas?
The prognosis of capillary hemangiomas is Most hemangiomas disappear later by undergoing spontaneous regression.