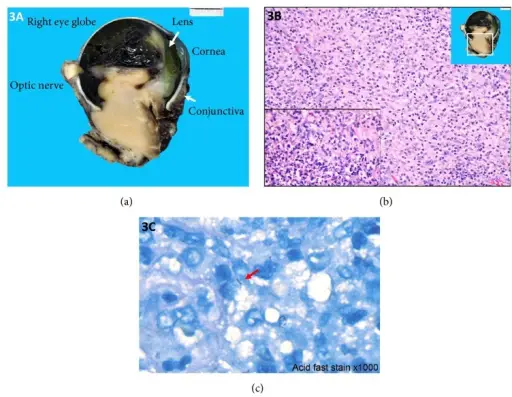
Panophthalmitis is inflammation that involves the choroid, retina, and sclera that extends into the orbit.
What is the Pathology of Panophthalmitis?
The pathology of panophthalmitis is often developed from endophthalmitis.
How does Panophthalmitis Present?
Panophthalmitis presents with hypopyon worsen, conjunctiva chemosis, eyelid edema, purulent discharge restricted and painful ocular movement.
How is Panophthalmitis Diagnosed?
Panophthalmitis is diagnosed by ultrasonography, and contrast enhanced MRI.
How is Panophthalmitis Treated?
Panophthalmitis is treated with intravitreal and periocular injection of combined antibiotics and dexamethasone.
What is the Prognosis of Panophthalmitis?
The prognosis of panophthalmitis is fair.