Dental caries may be defined as a bacterial disease of calcified tissues of teeth and is characterized by demineralization of the inorganic and destruction of the organic substance of the tooth.
What is the Pathology of Dental Caries?
The pathology of dental caries is:
-Etiology: The causing factors of dental caries are bacteria, time, susceptible tooth surface, and fermentable carbohydrates.
-Genes involved: DEFB1.
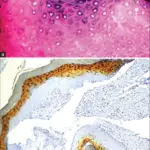
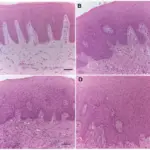
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to dental caries include enamel decay that may progress.
How does Dental Caries Present?
Patients with dental carries typically affect both males and females present at the age range of 10 years and above. Symptoms of dental caries are usually localized to the mouth. It includes holes in the surface of a tooth, pain when chewing, and sensitivity.
How are Dental Caries Diagnosed?
The diagnosis of carious lesions has been primarily a visual process, based principally on clinical inspection and review of radiographs.
How are Dental Caries Treated?
Dental caries are treated by fluoride treatments, fillings, crowns. root canals, tooth extractions.
What is the Prognosis of Dental Caries?
Dental caries prognosis depends on the health of the patient, maintenance of oral hygiene, and the extent and severity of dental caries. Overall the prognosis is fair.