Dentigerous cysts are a type of odontogenic cysts and generally occur in the ages of twenties or thirties. Dentigerous cyst always includes a tooth that cannot complete the eruption process and occurs around the crown by the fluid accumulation between the layers of the enamel organ.
What is the Pathology of Dentigerous Cyst?
The pathology of dentigerous cyst is:
-Etiology: The cause of dentigerous cyst is tooth enamel
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to dentigerous cyst includes the development from the accumulation of fluid (including glycosaminoglycans) between reduced enamel epithelium of dental follicle and crown of an unerupted tooth.
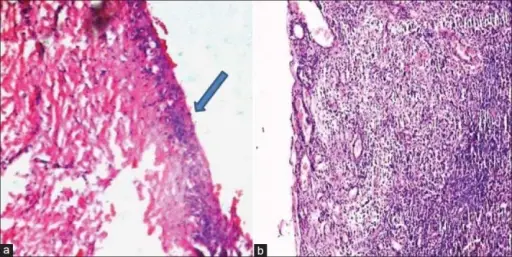
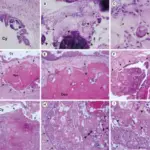
-Histology: The histology associated with dentigerous cyst shows fibrous connective tissue and hyperplastic non-keratinized epithelium, sometimes elongated interconnecting rete ridges.
How does the Dentigerous Cyst Present?
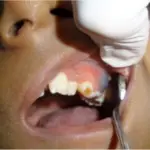
Patients with dentigerous cysts typically affect males and females present in the range of twenties and thirties. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with dentigerous cyst include swelling, sensitivity, displacement.
How is a Dentigerous Cyst Diagnosed?
Dentigerous cyst is diagnosed by radiographic findings, in combination with clinical information, can support a histomorphology diagnosis
How is Dentigerous Cyst Treated?
Dentigerous cyst is treated by enucleation of the entire cyst, marsupialization, removal of the cysts sparing the permanent tooth.
What is the Prognosis of Dentigerous Cyst?
The prognosis of dentigerous cyst is the excellent prognosis, almost never recurs with complete enucleation, however, follow up radiographic studies recommended.