Ameloblastoma is a benign tumor that is nonfunctional, unicentric, intermittent in growth, anatomically benign and persistent.
What is the Pathology of Ameloblastoma?
The pathology of ameloblastoma is:
-Etiology: The cause of ameloblastoma is the remnants of the enamel organ or dental lamina.
-Genes involved: TGFB1, TGFB3, and GDF15.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to ameloblastoma are ameloblastoma arise from remnants of ameloblast or dental lamina, dentigerous cysts, or basal layer of the oral mucosa.
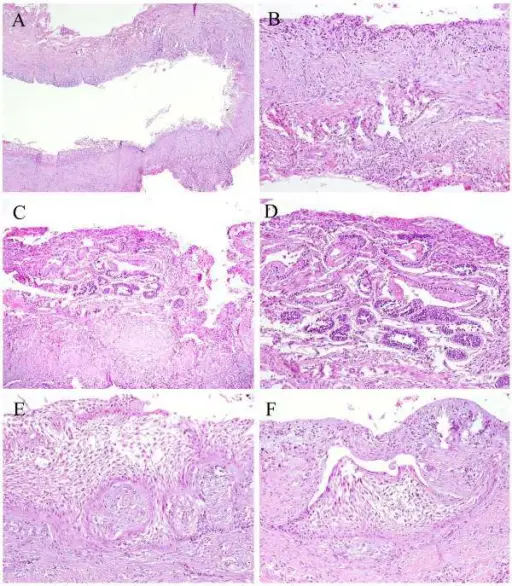
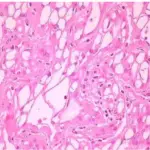
-Histology: The histology associated with ameloblastoma shows epithelial islands and cords of conventional ameloblastoma and the cystic epithelial lining of unicystic ameloblastoma.
How does Ameloblastoma Present?
Patients with Ameloblastoma typically affect males and females present in the age range of 40-50 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with ameloblastoma include painless jaw swelling and ulceration.
How is Ameloblastoma Diagnosed?
Ameloblastoma is diagnosed based on clinical, radiologic, and pathologic correlation
How is Ameloblastoma Treated?
Ameloblastoma is treated through segmental resection and through nonsurgical therapy.
What is the Prognosis of Ameloblastoma?
The prognosis of ameloblastoma is fair.