Clear-cell odontogenic carcinoma is a rare odontogenic tumor of the jaws.
What is the Pathology of Clear-Cell Odontogenic Carcinoma?
The pathology of clear-cell odontogenic carcinoma is:
-Etiology: The cause of clear cell odontogenic carcinoma is unknown.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to clear-cell odontogenic carcinoma is unknown.
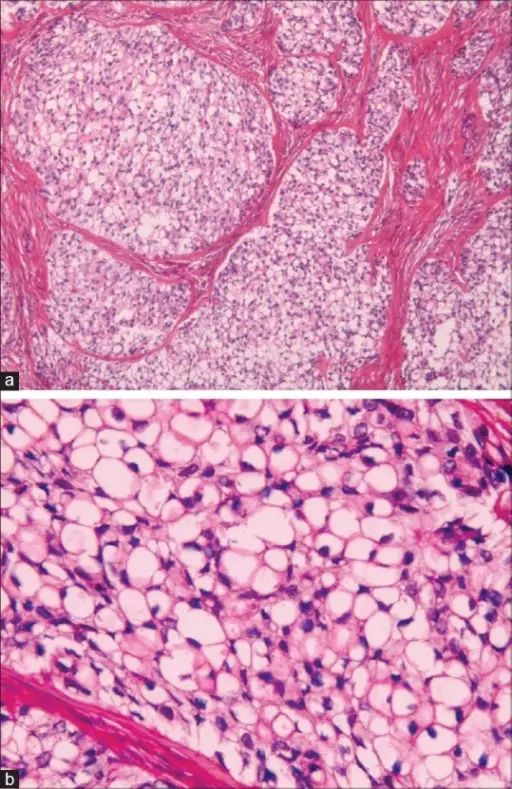
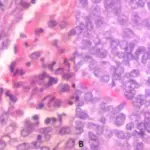
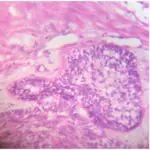
Histology: The histology associated with clear cell odontogenic carcinoma shows clear cells which are positive for cytokeratin and negative for vimentin and also negative for mucicarmine, which differentiates it from some of the other clear cell tumors such as mucoepidermoid carcinoma and renal carcinoma and calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor (CEOT).
How does Clear Cell Odontogenic Carcinoma Present?
Patients with Clear cell odontogenic carcinoma typically affect females present in the age range of 40-60 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with clear cell odontogenic carcinoma include swelling, tooth mobility, and pain.
How is Clear Cell Odontogenic Carcinoma Diagnosed?
Clear cell odontogenic carcinoma is diagnosed dependent on clinical, radiologic, and pathologic correlation.
How is Clear Cell Odontogenic Carcinoma Treated?
Clear cell odontogenic carcinoma is a treated combination of chemotherapy (Paclitaxel and carboplatin or irinotecan plus cisplatin) and surgical resection.
What is the Prognosis of Clear Cell Odontogenic Carcinoma?
The prognosis of clear cell odontogenic carcinoma is poor. The recurrence rate of 30% of resected and 87% of curetted/enucleated lesions.