Odontogenic fibroma is an extremely rare benign tumor that accounts for 0.1% of all odontogenic tumors. It appears as an asymptomatic expansion of the cortical plate of the mandible or maxilla.
What is the Pathology of Odontogenic Fibroma?
The pathology of odontogenic fibroma is:
-Etiology: The cause of odontogenic fibroma is unknown.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to odontogenic fibroma is a proliferation of mature odontogenic mesenchyme.
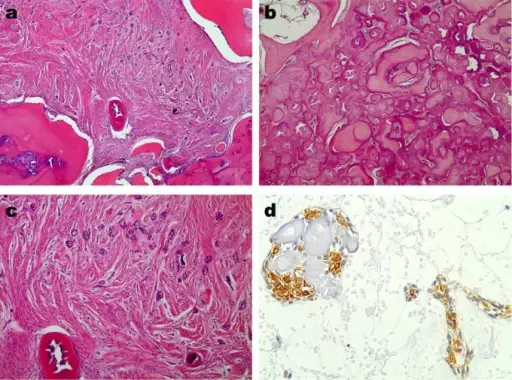
-Histology: The histology associated with odontogenic fibroma shows cellular fibro collagenous tissue with scattered, small, inactive odontogenic epithelium in strands, cords, or nests.
How does Odontogenic Fibroma Present?
Patients with Odontogenic Fibroma typically affect females present in the age range of 20-40 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with odontogenic fibroma include swelling and pain.
How is Odontogenic Fibroma Diagnosed?
Odontogenic fibroma is diagnosed depending on clinical, radiologic, and pathologic correlation.
How is Odontogenic Fibroma Treated?
Odontogenic fibroma is treated by excision, enucleation, and curettage
What is the Prognosis of Odontogenic Fibroma?
The prognosis of odontogenic fibroma depends on the type of odontogenic fibroma.