Leprosy (Hansen disease) infectious neuropathy is a chronic curable cause of neuropathy infection caused by the Mycobacterium leprae.
What is the Pathology of Leprosy (Hansen Disease) Infectious Neuropathy?
The pathology of leprosy (Hansen disease) infectious neuropathy is:
-Etiology: The cause of leprosy (Hansen disease) infectious neuropathy is Mycobacterium leprae.
-Genes involved: NA.
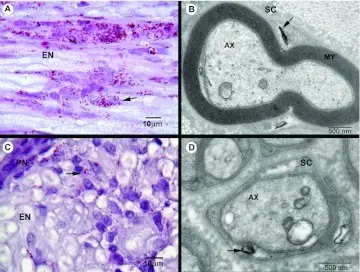
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to leprosy (Hansen disease) infectious neuropathy results from Schwann cells attacked by Mycobacterium leprae. This results in inflammation that injures the cutaneous nerves.
-Morphology: NA.
-Histology: The histology associated with leprosy (Hansen disease) infectious neuropathy shows nerve bundles with inflation, mononuclear cells, and granulomas.
How does Leprosy (Hansen Disease) Infectious Neuropathy Present?
Patients with leprosy (Hansen disease) infectious neuropathy are typically more common in males than females present at an age range of any age. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with leprosy (Hansen disease) infectious neuropathy include painless, non-itchy skin patches, diminished/loss of sensation, trophic ulcers and blisters, progressive wasting and weakness.
How is Leprosy (Hansen Disease) Infectious Neuropathy Diagnosed?
Leprosy (Hansen disease) infectious neuropathy is diagnosed through clinical presentations: laboratory studies- Skin biopsy to assess for acid-fast bacilli. Serologic assays detect phenolic glycolipid-1 and lipoarabinomannan.
How is Leprosy (Hansen Disease) Infectious Neuropathy Treated?
Leprosy (Hansen disease) infectious neuropathy is treated through medical management which may include multidrug regimen therapy (rifampicin, dapsone, and clofazimine). Surgery may be indicated.
What is the Prognosis of Leprosy (Hansen Disease) Infectious Neuropathy?
The prognosis of leprosy (Hansen disease) infectious neuropathy is fair with proper management.