Hereditary motor neuropathies is a progressive disorder of the nervous system that mostly affects the spinal cord.
What is the Pathology of Hereditary Motor Neuropathies?
The pathology of hereditary motor neuropathies is:
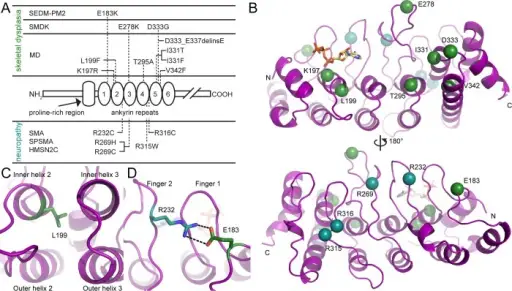
-Etiology: The cause of hereditary motor neuropathies is the malfunction of the heat shock proteins known as beta-1 and beta-8 triggered by mutation of the HSPB1 and HSPB8 genes.
-Genes involved: HSPB1, HSPB8 genes.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to hereditary motor neuropathies are atypical degeneration and development of the neural tissues.
-Morphology: NA.
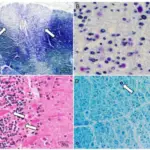
-Histology: The histology associated with hereditary motor neuropathies shows onion bulb formation on the affected nerve.
How does Hereditary Motor Neuropathies Present?
Patients with hereditary motor neuropathies typically are males present at the age range of childhood and young adulthood. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with hereditary motor neuropathies include fatigue, pain, lack of balance, loss of sensation, loss of hearing and sight, loss of reflexes.
How is Hereditary Motor Neuropathies Diagnosed?
Hereditary motor neuropathies are diagnosed with physical exam and history taking, electromyography, and genetic testing.
How is Hereditary Motor Neuropathies Treated?
Hereditary motor neuropathies are treated by physical therapy, use of braces, orthopedic surgery.
What is the Prognosis of Hereditary Motor Neuropathies?
The prognosis of hereditary motor neuropathies is fair since the symptoms occur later in life after the disease has progressed.