Neurofibromatosis Type 1 is an inherited condition that causes benign tumors to grow along the nerves characterized by the café au lait spots, lisch nodules.
What is the Pathology of Neurofibromatosis Type 1?
The pathology of neurofibromatosis type 1 is:
-Etiology: The cause of neurofibromatosis type 1 is genetic mutation.
-Genes involved: NF1 tumor-suppressor gene.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to neurofibromatosis type 1: mutation of the NF-1 gene causes loss of production of the protein that is responsible for increasing the chances of growth of tumors.
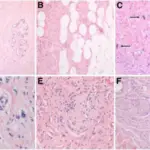
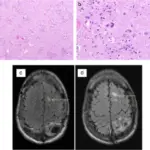
-Morphology: The morphology associated with neurofibromatosis type 1 shows large volumes of cortical and subcortical masses.
-Histology: The histology associated with neurofibromatosis type 1 shows mast cells, macrophages, endothelial cells, pericytes, and perineural cells.
How does Neurofibromatosis Type 1 Present?
Patients with neurofibromatosis type 1 typically are both male and female present at age range of 10 years, childhood. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with neurofibromatosis type 1 include café au lait, freckles on the armpits and groin, Lisch nodules, skeletal abnormalities e.g. osteopenia, and cardiovascular diseases,
How is Neurofibromatosis Type 1 Diagnosed?
Neurofibromatosis type 1 is diagnosed history taking, physical examination, CT scan, MRI, complete blood count, and biopsy.
How is Neurofibromatosis Type 1 Treated?
Neurofibromatosis type 1 is treated by mainly controlling the underlying symptoms. Other options include surgery, and pain medication.
What is the Prognosis of Neurofibromatosis Type 1?
The prognosis of neurofibromatosis is fair.