Polycythemia Vera is a stem cell syndrome characterized as a panhyperplastic, malignant, and neoplastic marrow disorder.
What is the Pathology of Polycythemia Vera?
The pathology of polycythemia vera is:
-Etiology: The cause of polycythemia vera is the tolerant neoplastic proliferation.
-Genes involved: JAK2V617F, JAK2 exon.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to polycythemia vera results from transmutations of the erythropoietin receptor leading to hyperresponsiveness to erythropoietin.
-Morphology: Platelet changes.
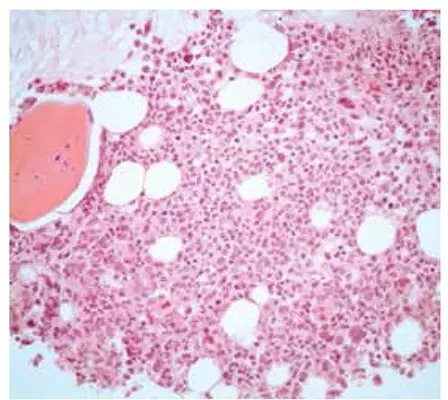
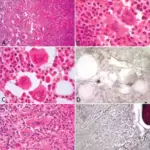
-Histology: The histology associated with polycythemia vera shows increased red cells
How does Polycythemia Vera Present?
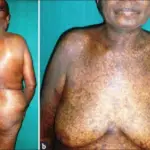
Patients with polycythemia vera typically higher in males present at an age range of 50 to 70 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with polycythemia vera include vertigo, headache, tinnitus, visual disturbances, dizziness, and angina pectoris.
How is Polycythemia Vera Diagnosed?
Polycythemia vera is diagnosed through laboratory studies- hematocrit and Hb level, serum erythropoietin level, and bone marrow biopsy indicating hypercellularity.
How is Polycythemia Vera Treated?
Polycythemia vera is treated through aspirin, and cytoreductive therapy. Surgical intervention such as splenectomy may be useful. Phlebotomy may be needed.
What is the Prognosis of Polycythemia Vera?
The prognosis of polycythemia vera is good with proper management of symptoms.