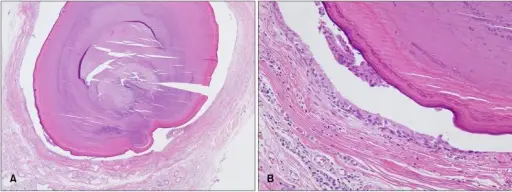
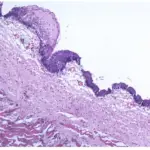
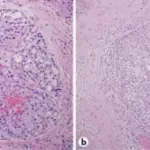
Sialolithiasis is a benign condition and it’s characterized by salivary stones obstructing the duct.
What is the Pathology of Sialolithiasis?
The pathology of sialolithiasis is:
-Etiology: The cause of sialolithiasis is a stone obstructing a salivary duct.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to sialolithiasis is unclear and may be due to multiple intracellular microcalculi that block salivary gland outflow.
-Histology: The histology associated with sialolithiasis shows varying degrees of acinar destruction. There may be inflammation and fibrosis.
How does Sialolithiasis Present?
Patients with sialolithiasis typically are male present at the age range of 30 – 60 years old. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with sialolithiasis include intermittent, pain and swelling of a salivary gland.
How is Sialolithiasis Diagnosed?
Sialolithiasis is diagnosed by physical exam and imaging.
How is Sialolitiasis Treated?
Sialolithiasis is treated by oral pain medication and antibiotics. Some circumstances may warrant surgical management.
What is the Prognosis of Sialolithiasis?
The prognosis of sialolithiasis is good.