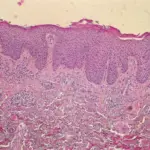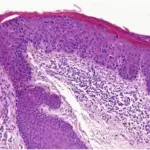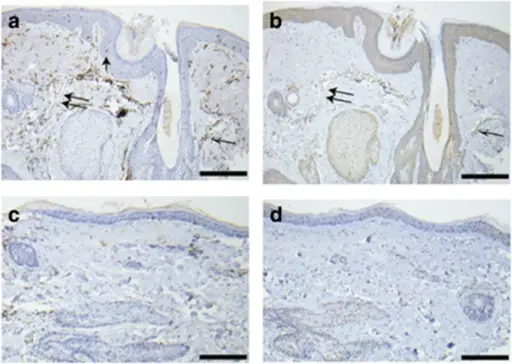
Rosacea. Genes associated with rs763035 are present in rosacea skin. (a) Rosacea skin from an individual of European descent and heterozygous for the minor allele at rs763035 immunostained with human leukocyte antigen-DRA antibody with a strong signal in the perifollicular inflammatory infiltrate (black and white arrow), epidermal Langerhans cells (single black arrow), and endothelial cells (double arrows). (b) Rosacea skin from the same individual as a and b immunostained with BTNL2 antibody showed mild-moderate staining in keratinocytes, perifollicular infiltrate (black and white arrow), and endothelial cells (double arrow). (c) Normal skin from the same individual stains with human leukocyte antigen-DRA antibody but lacks perifollicular infiltrate, numerous epidermal Langerhans cells, and dilated blood vessels seen in rosacea skin. (d) Normal skin from the same individual stained with BTNL2 antibody in keratinocytes but does not contain inflammatory infiltrate or dilated blood vessels. Negative controls were performed for all the tissues above by omitting either human leukocyte antigen-DRA or BTNL2 primary antibodies, and these displayed no staining (data not shown). Scale bar=100 μm. Assessment of the genetic basis of rosacea by genome-wide association study: Chang AL, Raber I, Xu J, Li R, Spitale R, Chen J, Kiefer AK, Tian C, Eriksson NK, Hinds DA, Tung JY - The Journal of investigative dermatology (2015). Not altered. CC.
Rosacea is the condition of the skin characterized by a spectrum of clinical signs and facial flushing.
What is the Pathology of Rosacea?
The pathology of rosacea is:
-Etiology: The cause of rosacea is corticosteroids uses, UV light exposure
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to rosacea are unknown.
-Morphology: The morphology associated with rosacea shows coarse skin, pustules, and erythema.
-Histology: The histology associated with rosacea shows granulomatous inflammation, lymphohistiocytic infiltrate, and multinucleated cells.
How does Rosacea Present?
Patients with rosacea are typically common in males than females present at an age range of 12 to 24. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with rosacea include facial flushing, erythema and telangiectasia, inflamed papules, and pustules.
How is Rosacea Diagnosed?
Rosacea is diagnosed through clinical examination and biopsy to role out cutaneous diseases.
How is Rosacea Treated?
Rosacea is treated through laser treatment, surgery, identification of deterrence.
What is the Prognosis of Rosacea?
The prognosis of rosacea is fair. Has chronic progressive course in some patients.