Tinea is a superficial fungal condition of the skin is limited to the stratum corneum, caused chiefly by dermatophytes Tinea capitis.
What is the Pathology of Tinea?
The pathology of tinea is:
-Etiology: The cause of tinea is dermatophytes.
-Genes involved: None.
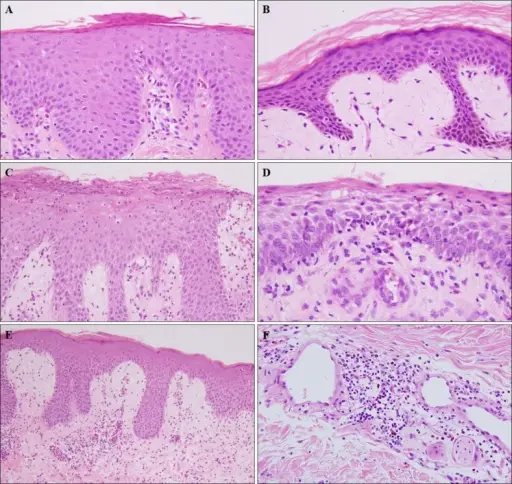
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to tinea involve invasion into keratinized tissue. They, persist and infect the stratum corneum of the epidermis, and hardly do they penetrate below beyond the epidermis.
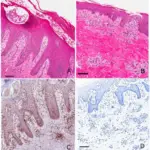
-Morphology: The morphology associated with tinea shows variable features reliant on the organism antigenic properties, and the grade of bacterial superinfection.
-Histology: The histology associated with tinea shows eczematous dermatitis, stain bright pink to red mucopolysaccharides fungal cell walls.
How does Tinea Present?
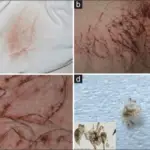
Patients with tinea are typically more common in males present at an age range of any age. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with tinea include symptomless, frequently hairless patches of skin, mild erythema, scale, crust formation.
How is Tinea Diagnosed?
Tinea is diagnosed through examination, microscopic examination, wood light (UV light) examination skin scraping, fungal culture, and biopsy.
How is Tinea Treated?
Tinea is treated through medical therapy antifungals, proper hygiene for prevention.
What is the Prognosis of Tinea?
The prognosis of tinea is good. Resolves without sequelae in 1-2 weeks of treatment.