Erythema Induratum is an uncommon type of panniculitis affecting principally menopausal women and adolescents.
What is the Pathology of Erythema Induratum?
The pathology of erythema induratum is:
-Etiology: The cause of erythema induratum is unknown though associated with vasculitis affecting deep vessels.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to erythema induratum not well understood.
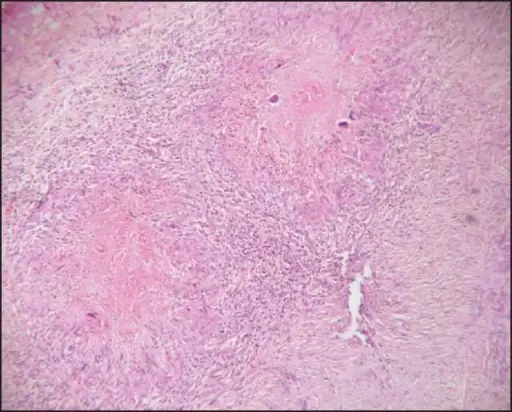
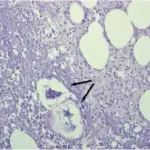
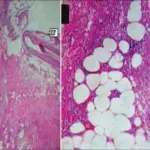
-Morphology: The morphology associated with erythema induratum shows necrotizing vasculitis affecting the deep dermis and subcutis arteries and veins.
-Histology: The histology associated with erythema induratum shows granulomatous inflammation, zones of caseous necrosis involving fat lobule.
How does Erythema Induratum Present?
Patients with erythema induratum typically common in females than males present at age range of 13 to 60 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with erythema induratum include tender, erythematous nodules on lower limbs.
How is Erythema Induratum Diagnosed?
Erythema Induratum is diagnosed through the clinical presentation, laboratory studies-such as LFTs, ESR, Hepatitis C virus serology, CBC count, PCR for detection of M tuberculosis.
How is Erythema Induratum Treated?
Erythema induratum is treated through medical management of underlying symptoms nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory, potassium iodide, and tetracyclines.
What is the Prognosis of Erythema Induratum?
The prognosis of erythema induratum is good under proper treatment and management.