Seborrheic dermatitis is a disorder of papulosquamous patterned on the areas of the scalp, face, and trunk with sebum-rich.
What is the Pathology of Seborrheic Dermatitis?
The pathology of seborrheic dermatitis is:
-Etiology: The cause of seborrheic dermatitis is unknown.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to seborrheic dermatitis is unknown.
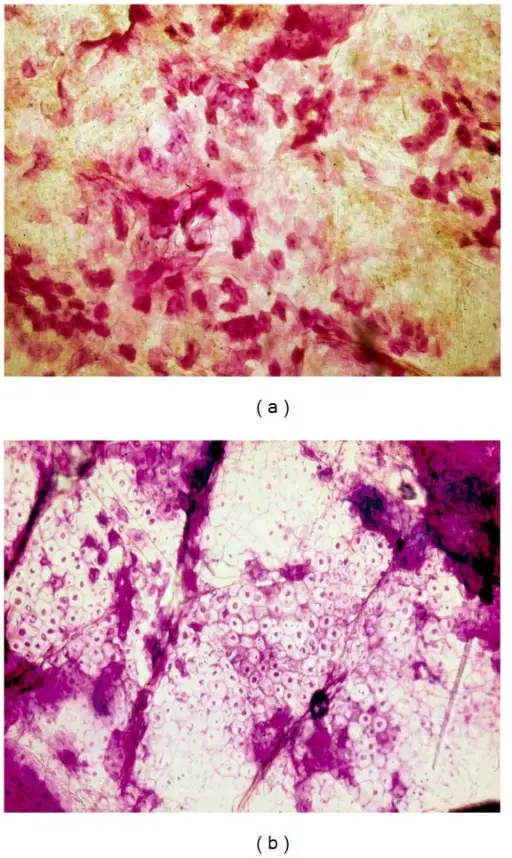
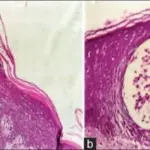
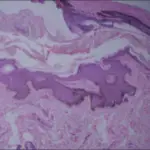
-Morphology: The morphology associated with seborrheic dermatitis shows scaling over red, inflamed skin.
-Histology: The histology associated with seborrheic dermatitis shows parakeratosis containing neutrophils and serum.
How does Seborrheic Dermatitis Present?
Patients with seborrheic dermatitis are typically more common in males than females present at an age range of 40 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with seborrheic dermatitis include burning, scaling, itching, candidal overgrowth, and blepharitis.
How is Seborrheic Dermatitis Diagnosed?
Seborrheic dermatitis is diagnosed based on clinical presentations, laboratory studies of the skin biopsy.
How is Seborrheic Dermatitis Treated?
Seborrheic dermatitis is treated through with topical corticosteroids, antifungal, and shampooing.
What is the Prognosis of Seborrheic Dermatitis?
The prognosis of seborrheic dermatitis is good.