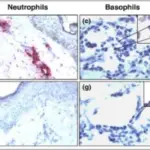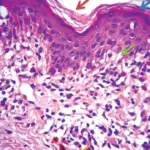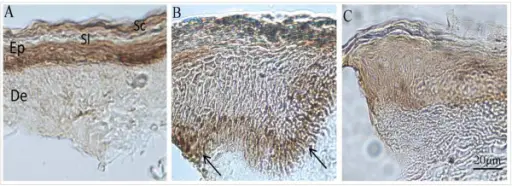
Chronic Inflammatory Dermatoses. Immunohistochemical micrograph for TGF-β1 in human skin. A, a section from a healthy person showing discrete cell levels in the stratum corneum (Sc), stratum lucidum (Sl), epidermis (Ep) and dermis (De); TGF-β1 was strongly expressed in epidermis of healthy skin. No immunoreactivity is seen in the dermis of healthy skin. B, TGF-β1 is intensely expressed in the basal layer of the epidermis of a chronic dermatitis patient. C, Epidermis of a chemically injured person weakly showed immunoreactivity for TGF-β1 throughout the entire epidermis. Loss of expression of TGF-βs and their receptors in chronic skin lesions induced by sulfur mustard as compared with chronic contact dermatitis patients: Khaheshi I, Keshavarz S, Imani Fooladi AA, Ebrahimi M, Yazdani S, Panahi Y, Shohrati M, Nourani MR - BMC dermatology (2011). Not altered. CC.
Chronic inflammatory dermatoses are tenacious skin conditions that exhibit their most characteristic features for a long time months to years.
Examples of chronic inflammatory dermatoses include:
- Lichen planus
- Psoriasis
- Seborrheic dermatitis
- Hidradenitis suppurativa