Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans is a neoplasm that can be intermediate to low-grade malignancy and invades other tissues like the muscles and bones.
What is the Pathology of Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans?
The pathology of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans is the study of the soft tissue of the skin that are cancerous.
-Etiology: The cause of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans is a chromosomal deviation from the normal,
-Genes involved: COL1A, PDGFB.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans is a result of increased proliferation of one of the types of cells found in the human body.
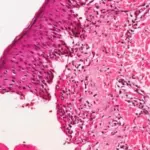
-Morphology: The morphology associated with dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans shows irregular nodules that vary in size and color (pink to red to brownish) and are very firm on touch.
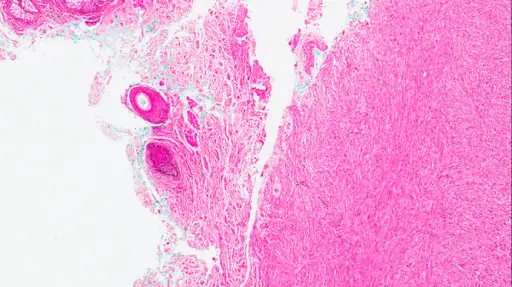
-Histology: The histology associated with dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans shows irregular high cellularity, spindle-shaped cells, has a storiform growth pattern, and a diffuse infiltrative pattern.
How does Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans Present?
Patients with dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans are typically male with a 57% rate and occur mostly in adults with a mean age of 20-50 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans include an asymptomatic, sclerotic plaque, and when it is enlarging it has fast growth and an ulcer is formed.
How is Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans Diagnosed?
The dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans are diagnosed through physical examination, chest radiography in case metastasis is questioned and an MRI may be requested too.
How is Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans Treated?
The dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans are treated surgical removal and radiotherapy as an adjunct and molecular targeted drug the imatinib mesylate.
What is the Prognosis of Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans?
The prognosis of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans is poor mainly in those with a mean age of 50-years-old.