Liposarcoma is a rare mesenchymal neoplasm that involves deep soft tissues.
What is the Pathology of Liposarcoma?
The pathology of liposarcoma is:
-Etiology: The cause of liposarcoma is still unknown.
-Genes involved: An abnormality of band 12q13, FUS-CHOP.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to liposarcoma are fusion proteins created by chromosomal abnormalities. has been associated with the development of liposarcomas.
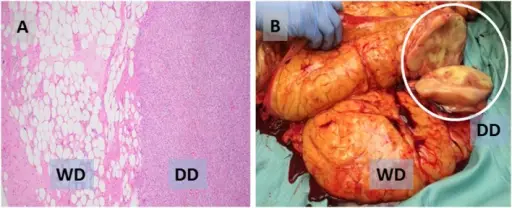
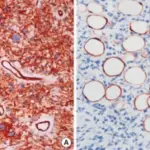
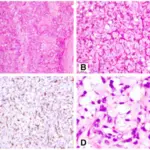
-Histology: The histology associated with liposarcoma shows mature adipocytes with a variable amount of fibrous stroma containing atypical nuclei.
How does Liposarcoma Present?
Patients with liposarcoma are typically males slightly more than females present at an age range of about 50 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with liposarcoma are usually not detectable until the tumor is large and impinges on neighboring structures, causing tenderness, pain, or functional disturbances.
How is Liposarcoma Diagnosed?
Liposarcoma is diagnosed by radiographic imaging and biopsy.
How is Liposarcoma Treated?
Liposarcoma is treated by surgical excision. Adjuvant radiation therapy or chemotherapy may be needed.
What is the Prognosis of Liposarcoma?
The prognosis of a liposarcoma depends on several factors but is typically fair with proper management.