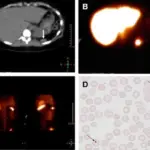
Accessory spleen is a congenital deviation characterized by the ectopic splenic tissue detached from the body of the spleen. Accessory spleens result from the failure of union of the primordial splenic buds at dorsal mesogastrium at the 5th-week of fetal life. Accessory spleens are diagnosed by imaging.
What are Accessory Spleens?
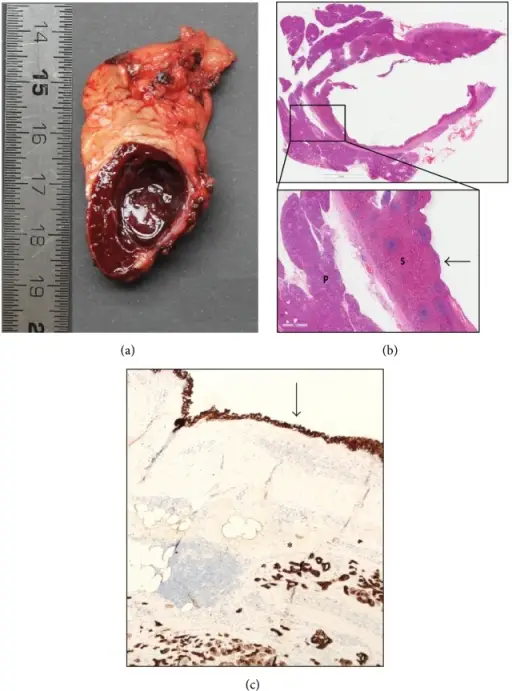
Accessory Spleens. (a) Photograph of the cut gross specimen showing well-defined splenic tissue with a unilocular cyst. (b) Hematoxylin-eosin staining showing pancreatic parenchyma (P) and adjacent splenic parenchyma (S) and the cyst wall lined by multilayered epithelium without atypia (arrow). (c) Cytokeratin 5 staining showing positivity in the cyst lining (arrow) and in surrounding pancreatic parenchyma (asterisk) indicating epithelial lining. Rare Case of an Epithelial Cyst in an Intrapancreatic Accessory Spleen Treated by Robot-Assisted Spleen Preserving Distal Pancreatectomy. Case Reports in Gastrointestinal Medicine. Not Altered. CC.