Splenic lymphoma is an indolent B-cell malignancy typically relating to the spleen, bone marrow, and blood. It is one of the distinct types of marginal zone lymphomas.
What is the Pathology of Splenic Lymphoma?
The pathology of splenic lymphoma is:
-Etiology: The cause of splenic lymphoma is not usually clear, although it has been linked with those who have been detected with the hepatitis C virus (HCV) and/or other autoimmune syndromes.
-Genes involved: BIRC3-MALT1, Bcl-10, MALT1, and FOXP1.
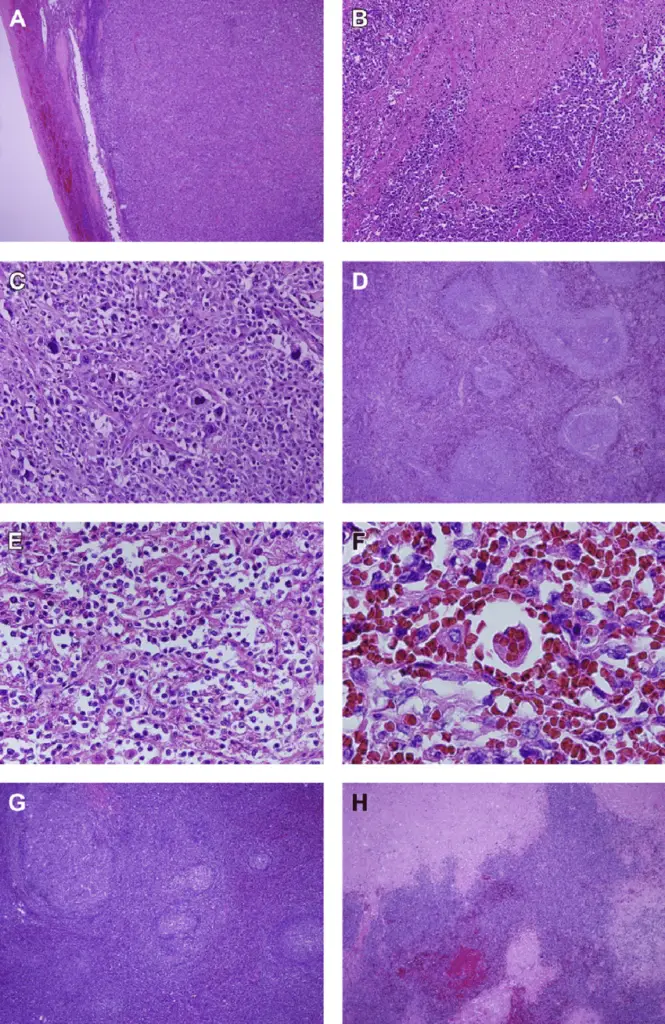
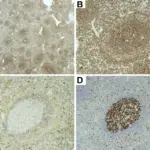
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to splenic lymphoma is, lymphoma grows in the white pulp with the biphasic picture. The Medium-size monocytoid B-cells are prearranged into the pale ring around the follicle containing an MZ pattern, while small centrocyte-like cells obliterate the mantle zone and take possession of the germinal centers. An Inconstant degree of plasmacytic diversity might be present. Lymphoma cells might comprise the red pulp irregularly or diffusely, with successive spread to the sinuses.
How does Splenic Lymphoma Present?
Patients with splenic lymphoma typically, affect both men and women, although more common in men. Present at an age range of middle-aged or elderly, with the average age at diagnosis of 65 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with splenic lymphoma include an enlarged spleen (splenomegaly), B symptoms (night sweats, persistent fevers, unexplained weight loss), thrombocytopenia, and anemia.
How is Splenic Lymphoma Diagnosed?
Splenic lymphoma is diagnosed can be detected using a combination of blood tests complete blood count (CBC) and a bone marrow biopsy.
How is Splenic Lymphoma Treated?
Splenic lymphoma is treated through surgical therapy (splenectomy) followed by long-term antibiotic treatment, chemotherapy regimen. Other standard treatment options include radiotherapy to the spleen, rituximab with or without chemotherapy, or chemo-immunotherapy combinations, rituximab, and chlorambucil. Treatment varies depending on the stage and what symptoms are present.
What is the Prognosis of Splenic Lymphoma?
The prognosis of splenic lymphoma is good it responds well to treatment. However, since it is indolent lymphoma, splenic lymphoma often relapses.