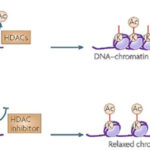
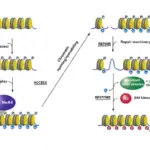
Histone methylation is when methyl groups are transferred to amino acids of histone proteins, it can either increase or decrease transcription of genes, depending on which amino acids in the histones are methylated. Histone methylation typically results in decreased expression of the genes in the methylated region.
What is Histone Methylation?
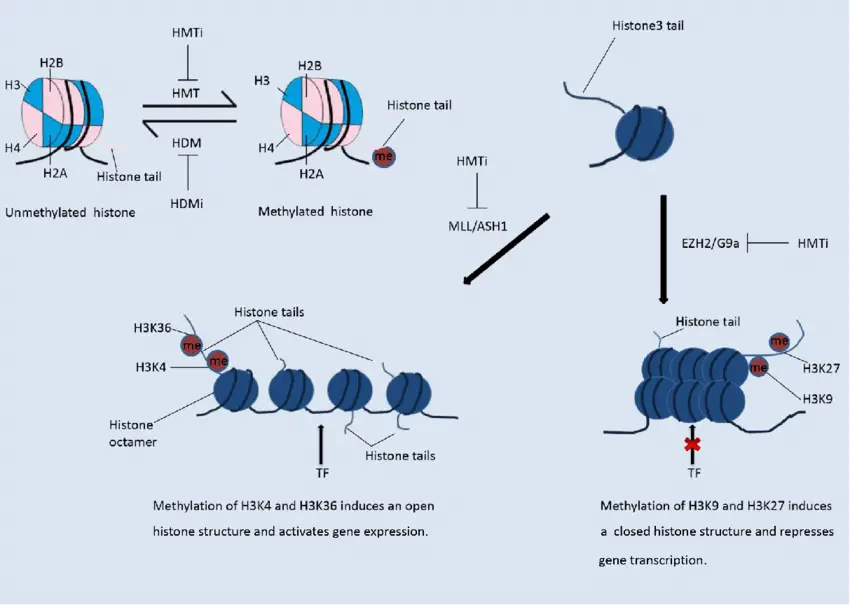
Histone methylation. The methylation status of a histone is reversible. In contrast to histone acetylation, methylation of histones on different residues suppresses or enhances gene transcription. Methylation of H3K4 and H3K36 induces an open histone structure and hence promotes transcription. Methylation of H3K9 and H3K27 induces a compacted histone structure and hence suppresses gene transcription. Not altered. CC.
Enhancing the Anticancer Efficacy of Immunotherapy through Combination with Histone Modification Inhibitors
Wanyu Sun, Shuting Lv, Hong Li, Wei Cui and Lihui Wang