Elastin is a key protein of the extracellular matrix which is highly elastic and present in connective tissue them to resume their shape after stretching or contracting.
What is Elastin?
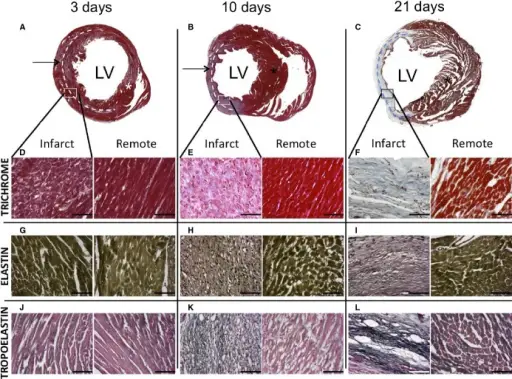
Elastin. Trichrome staining of heart sections at 4, 11, and 22 (A through C) post-MI. Infarcted and remote areas are identified with an arrow and a star, respectively. The dashed lines highlight the extension of the areas of infarct. High magnification (×40) of infarcted and remote areas is shown for trichrome (D through F), elastin (G through I), and tropoelastin (J through L). While collagen appears in blue, elastin and tropoelastin are identified as black filaments. Quantification analysis was performed to determine the amount of tropoelastin and elastin with respect to the infarcted area. Little to no elastin was found at any time point, whereas 8% and 20% of tropoelastin was detected at 11 and 22 days post-MI, respectively. Scale bars, 50 μm; n =3 for 3 days and 10 days post-MI; n =6 for 21 days post-MI. LV indicates left ventricular; MI, myocardial infarction. Assessment of Myocardial Remodeling Using an Elastin/Tropoelastin Specific Agent with High Field Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). Protti A, Lavin B, Dong X, Lorrio S, Robinson S, Onthank D, Shah AM, Botnar RM - Journal of the American Heart Association (2015). Not Altered. CC.