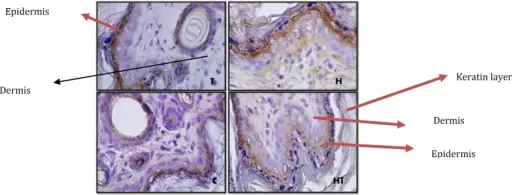
Hypothyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland is not able to produce enough thyroid hormone required for the body. Hypothyroidism may occur due to decreased thyroid hormone due to functional or structural issues. Hypothyroidism may also be due to autoimmune, congenital, or iatrogenic causes.
What is the Pathology of Hypothyroidism?
The pathology of hypothyroidism may be due to destruction of the thyroid gland which leads to decreased secretion of thyroid hormones T3 and T4.
How does Hypothyroidism Present?
Hypothyroidism commonly presents with symptoms that include fatigue, cold sensitivity, dry skin, muscle cramps, voice changes, and constipation. Advanced hypothyrodism signs may include sleep apnea, and pituitary hyperplasia.
How is Hypothyroidism Diagnosed?
Hypothyroidism is diagnosed by measuring serum thyrotropin (TSH), T3, and T4 levels.
How is Hypothyroidism Treated?
Hypothyroidism is typically treated with thyroid hormone replacement therapy such as L-thyroxine.
What is the Prognosis of Hypothyroidism?
The prognosis of hypothyroidism is good with early treatment if the disease hasn’t progressed to myxedema coma.