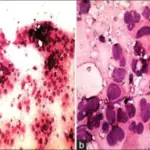
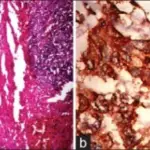
Follicular carcinoma is the carcinoma of the thyroid with follicular differentiation but no papillary nuclear features.
What is the Pathology of Follicular Carcinoma?
The pathology of follicular carcinoma is:
-Etiology: The cause of follicular carcinoma is old age, radiation exposure, and iodine deficiency.
-Genes involved: RAS.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to follicular carcinoma involves point mutations that result in dysregulation of the phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase (PI3K)/AKT signaling pathway.
-Histology: The histology associated with follicular carcinoma shows neoplastic follicular cells.
How does Follicular Carcinoma Present?
Patients with follicular carcinoma are typically females. present at the age range of 40-60 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with follicular carcinoma include difficulty breathing, hoarseness, difficulty swallowing persistent cough, voice changes, and vocal cord paralysis.
How is Follicular Carcinoma Diagnosed?
Follicular carcinoma is diagnosed using blood testing.
How is Follicular Carcinoma Treated?
Follicular carcinoma is treated thyroidectomy or lobectomy.
What is the Prognosis of Follicular Carcinoma?
The prognosis of follicular carcinoma is poor overall however, the prognosis is found to be good in females with a survival of 5 years.