Congenital Heart Defects Pathology Video
Congenital Heart Defects
Congenital heart defects occur throughout embryogenesis (usually weeks 3 through 8).
Congenital heart defects are observed in 1% of live births.
Most congenital heart defects are incidental and not clinically significant.
Congenital heart defects frequently cause shunting between the right (pulmonary) and left (systemic) circulations.
The shunt can gradually reverse, even though defects with left-to-right shunting may be largely asymptomatic at birth.
Pulmonary hypertension and pulmonary hypertrophy are caused by increased flow via the pulmonary circulation.
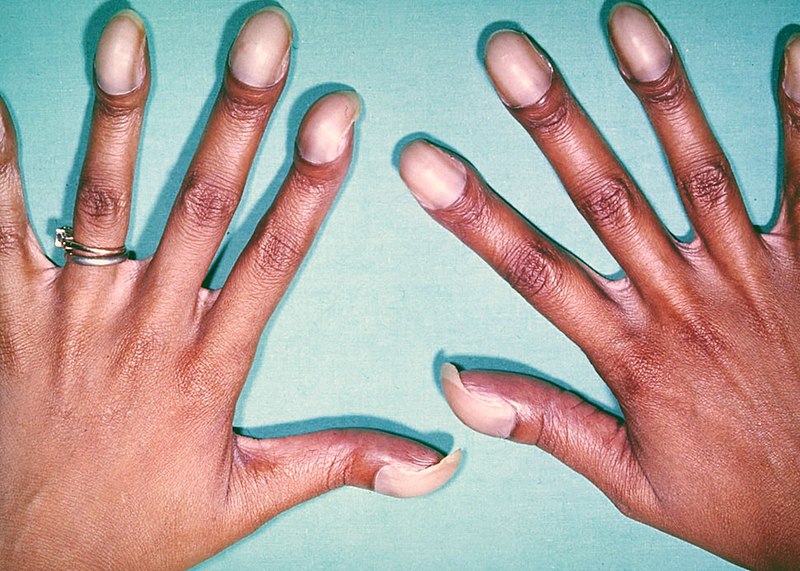
The shunt gradually reverses due to increased pulmonary resistance, causing late cyanosis (Eisenmenger syndrome) along with right ventricular hypertrophy, polycythemia, and clubbing.
Cyanosis is typically the first sign of right-to-left shunting defects soon after birth.
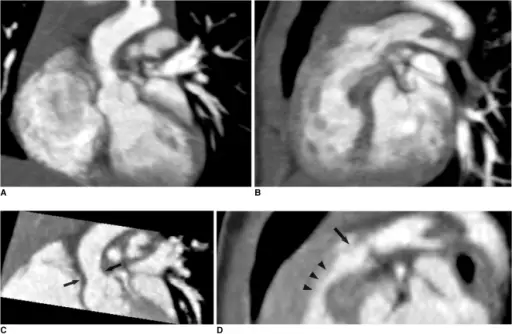
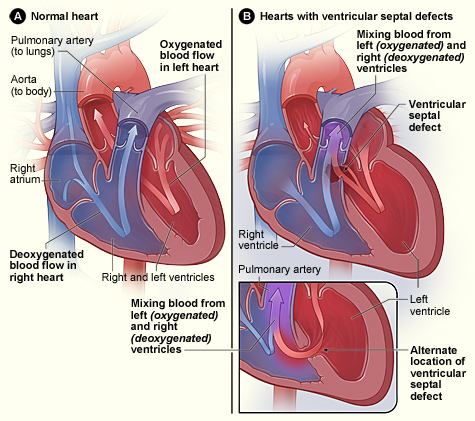
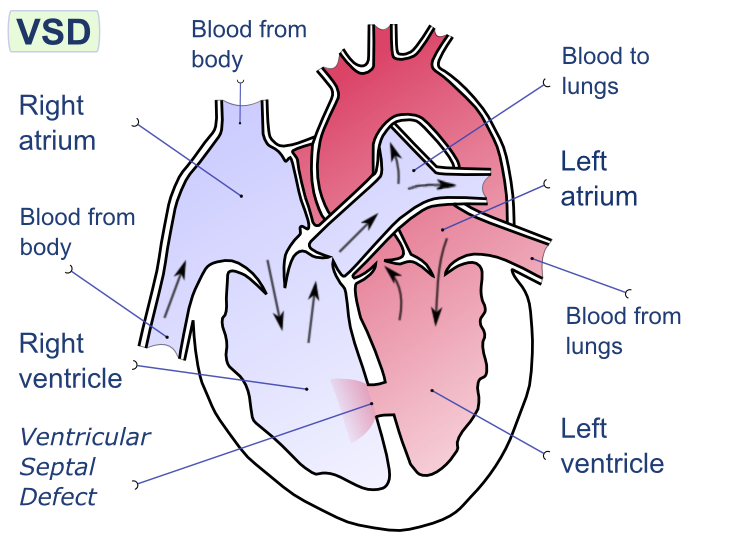
Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD)
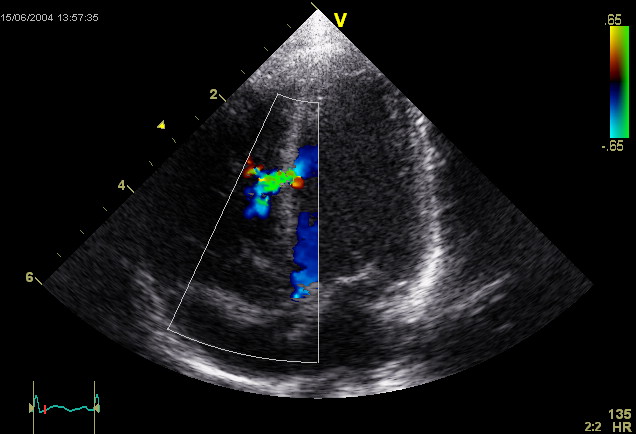
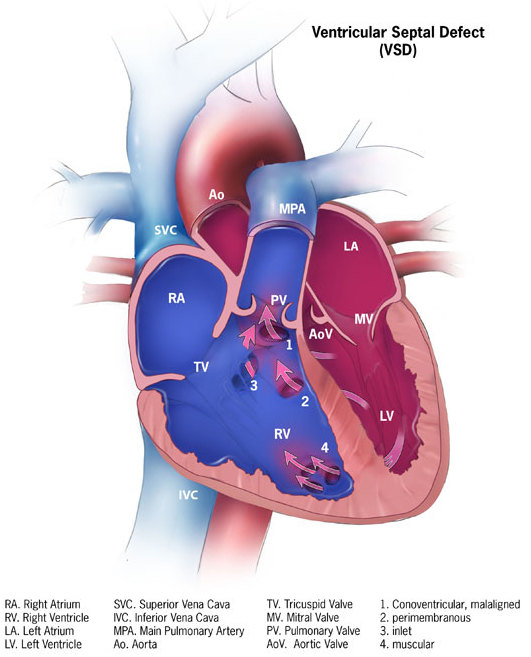
A ventricular septal defect is a flaw in the wall that separates the right and left ventricles, or septum.
Ventricular septal defect is the most common congenital cardiac condition.
Ventricular septal defect is inextricably linked to fetal alcohol syndrome.
Ventricular septal defect results in a shunt from left to right.
Age at presentation and defect size both depend on the ventricular septal defect size.
Large ventricular septal defect can cause Eisenmenger syndrome.
Treatment of large ventricular septal defect involves surgery.
Small ventricular septal defects are frequently asymptomatic.
Small flaws might naturally close.
Atrial Septal Defect (ASD)
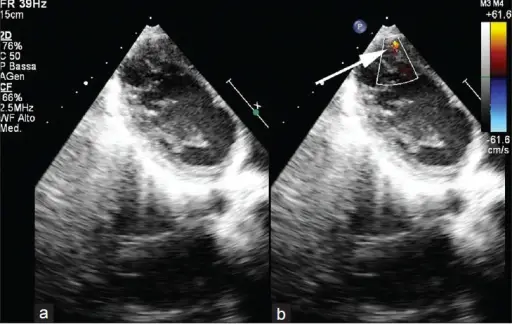
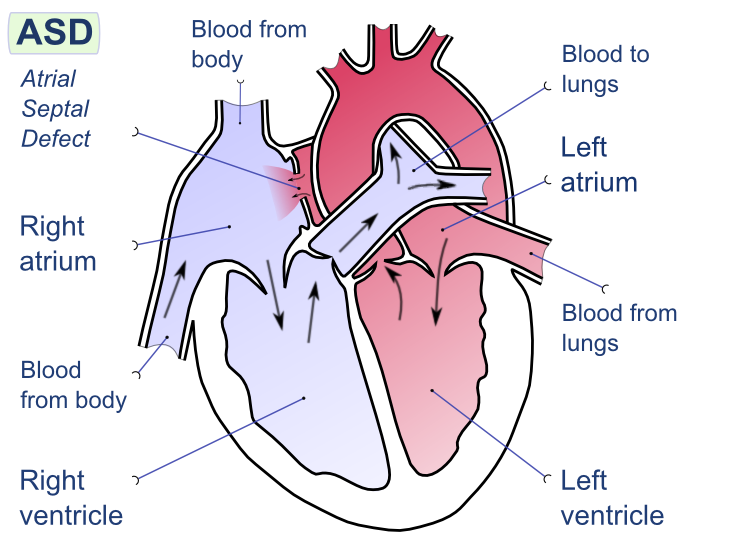
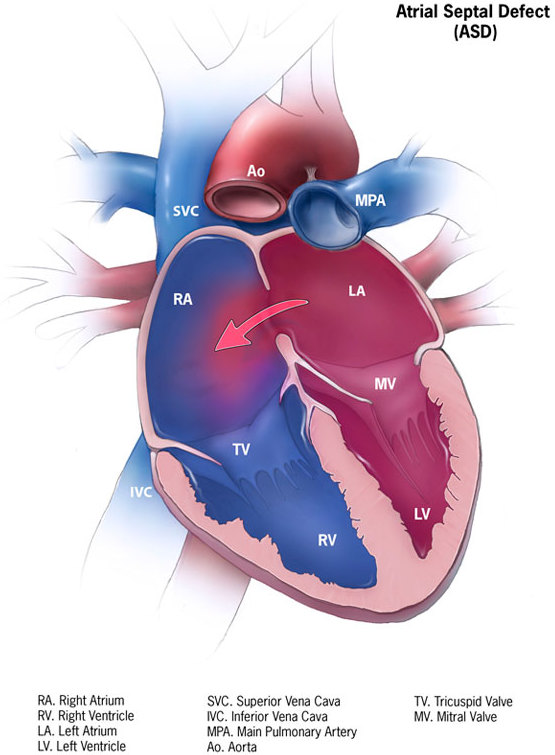
An atrial septal defect (ASD) is a hole in the wall that separates the right and left atria.
Ostium secundum is the most prevalent (90 percent of cases) cause of atrial septal defect (ASD).
Down syndrome is linked to the osteoid primum type of atrial septal defect (ASD).
An atrial septal defect (ASD) results in a divided S2 and a left-to-right shunt on auscultation (increased blood in right heart delays closure of pulmonary valve).
Paradoxical emboli are potential complications of atrial septal defects (ASD).
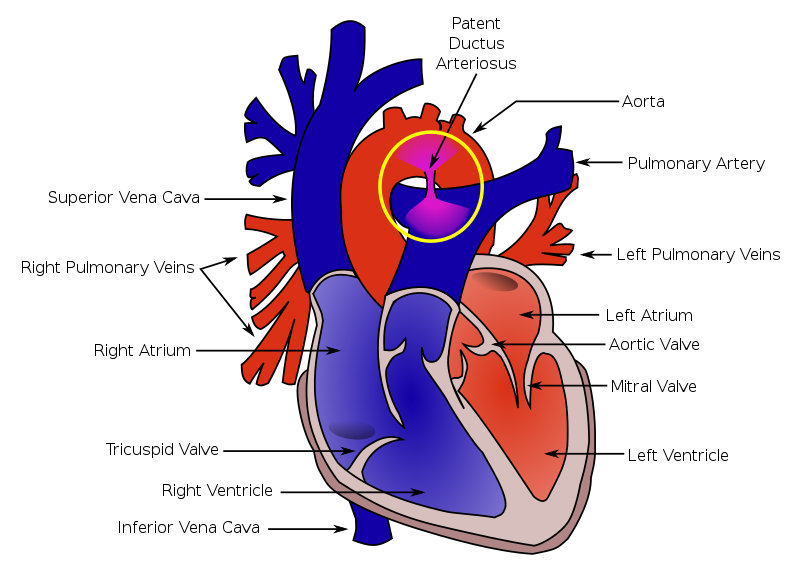
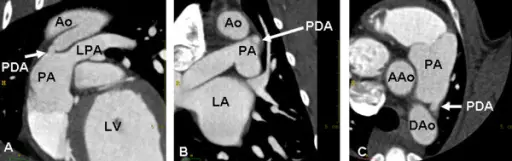
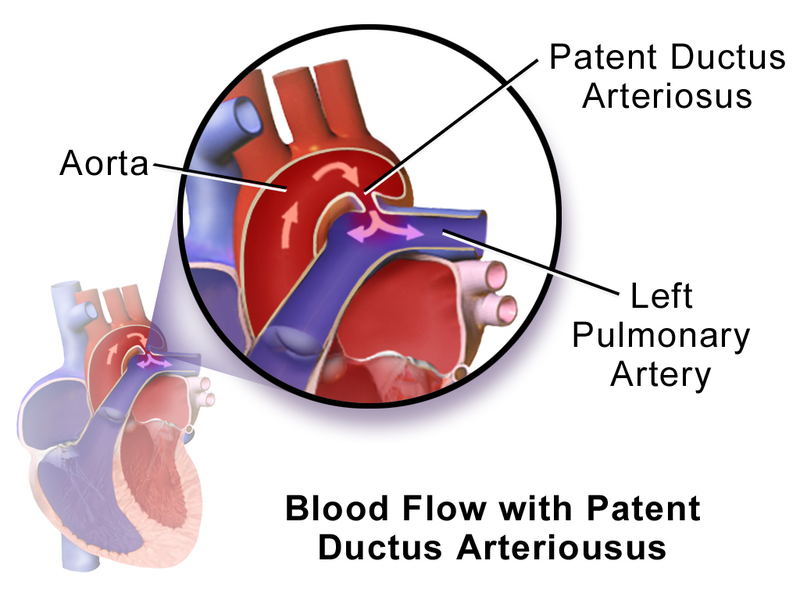
Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA)
A patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) results from failure of the ductus arteriosus close.
Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) is linked to congenital rubella.
Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) results in a left-to-right shunt between the pulmonary artery and the aorta.
The ductus arteriosus generally diverts blood away from the lungs and toward the aorta during development.
Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) is typically asymptomatic at birth with a holosystolic ‘machine-like’ murmur.
Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) may result in lower extremity cyanosis and Eisenmenger syndrome.
Treatment of patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) involves indomethacin, which decreases prostaglandin E1 (PGE1), resulting in PDA closure.
Note that PGE1 maintains patency of the ductus arteriosus.
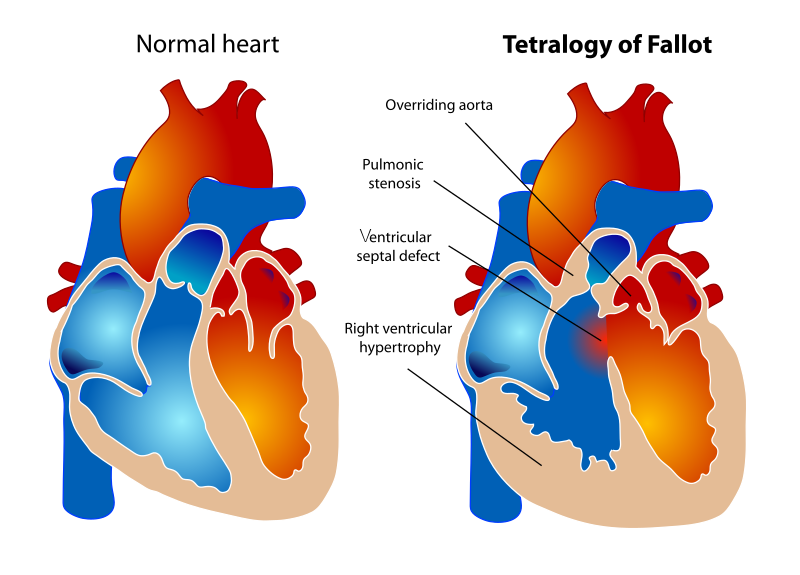
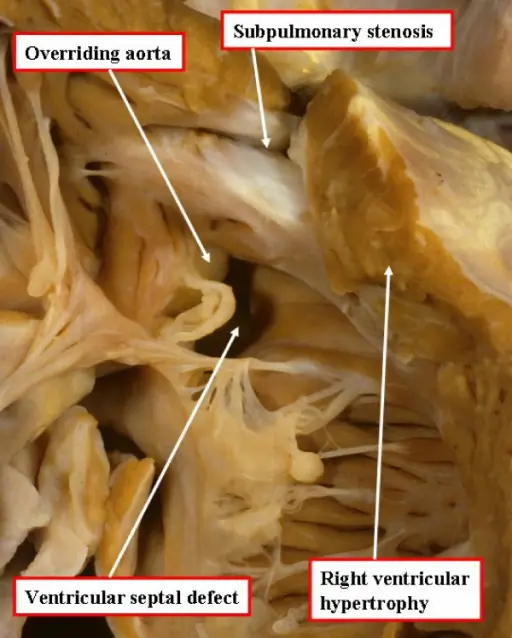
Tetralogy of Fallot (ToF)
Tetralogy of Fallot (ToF) is a congenital cardiovascular anomaly that includes:
- Right ventricular outflow tract stenosis
- Right ventricular hypertrophy
- Ventricular septal defect (VSD)
- An overriding aorta
Early cyanosis is caused by right-to-left shunting, and the degree of stenosis dictates how much shunting and cyanosis is present.
In response to a cyanotic spell, patients with tetralogy of Fallot (ToF) are taught to squat because:
- Artery resistance is increased.
- Reduces shunting and increases blood flow to the lungs
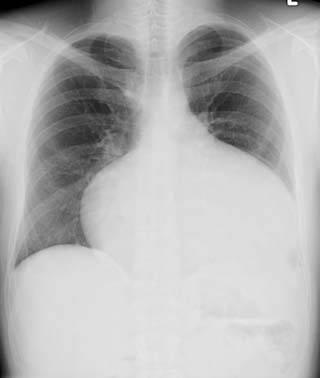
Tetralogy of Fallot (ToF) radiology of the heart shows a “boot-shaped” heart.
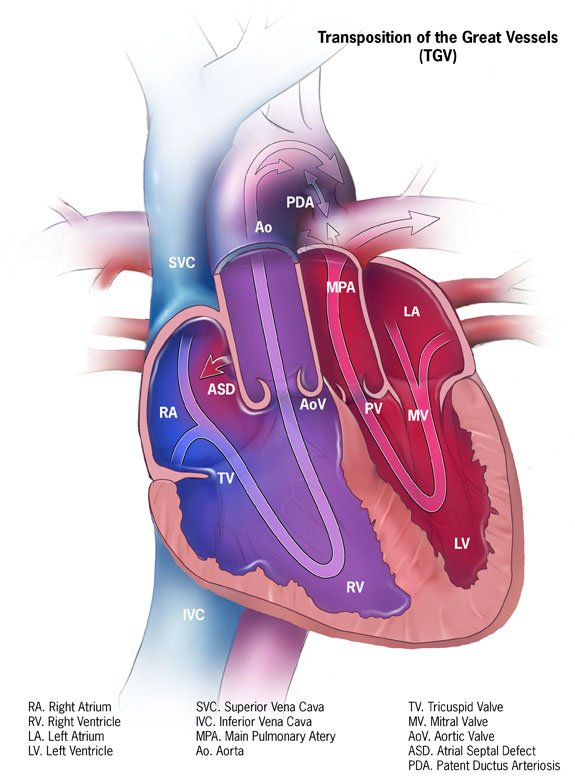
Transposition of the Great Vessels
Transposition of the great vessels is characterized by the aorta and pulmonary artery emerging from the right and left ventricles, respectively.
Gestational diabetes is a risk factor for transposition of the great vessels.
Transposition of the great vessels has an early cyanotic presentation.
Systemic and pulmonary circuits do not interact.
After birth, shunt formation (enabling blood to mix) is necessary for survival.
Prostaglandin E1 (PGE1) can be given to keep a patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) open until a permanent surgical repair is made.
Transposition of the great vessels results in left ventricular atrophy and right ventricle enlargement.
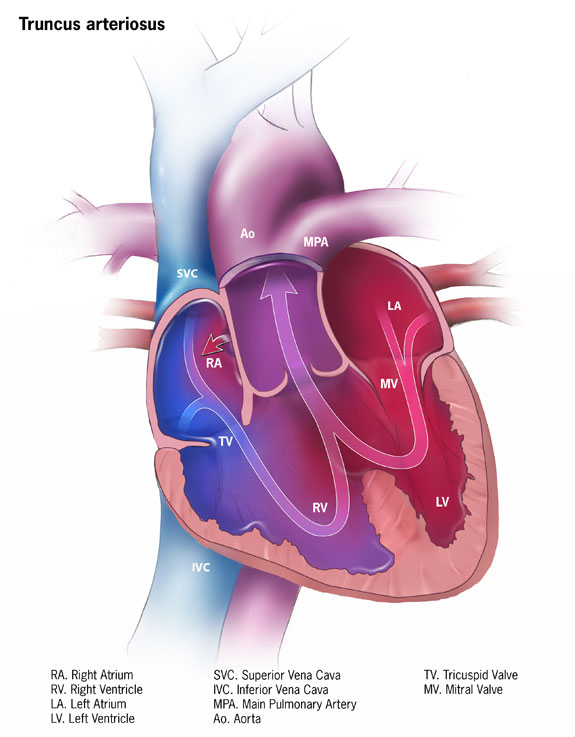
Truncus Arteriosus
Truncus arteriosus is characterized by the emergence of a single, sizable vessel from both ventricles.
Truncus arteriosus is due to a failure of division.
Truncus arteriosus has an early cyanotic presentation.
Before the pulmonary and aortic circulations separate, deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle and oxygenated blood from the left ventricle combine.
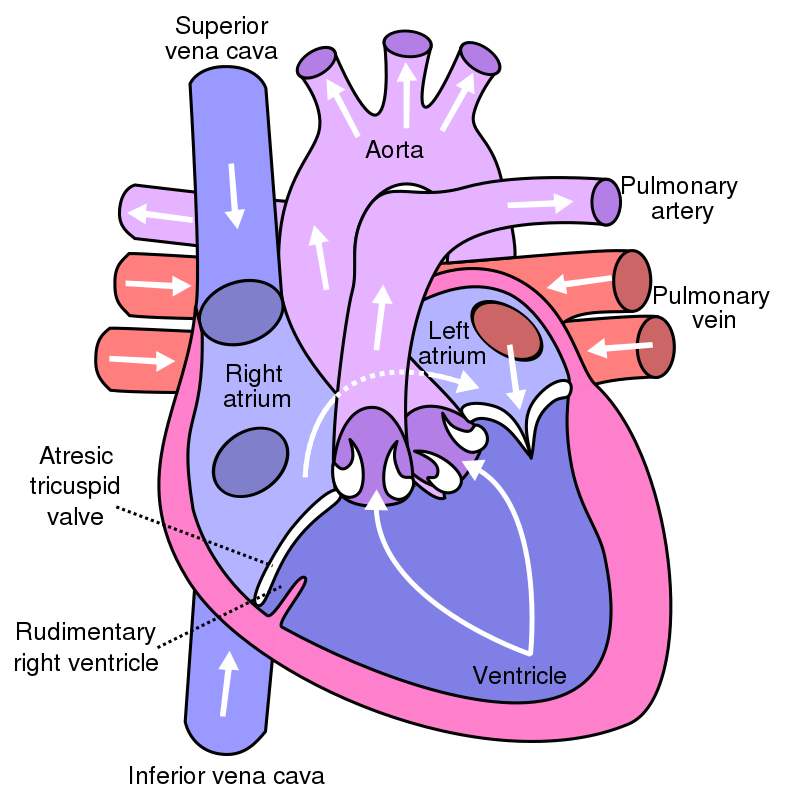
Tricuspid Atresia
Tricuspid atresia is due to failure of the orifice of the tricuspid valve to form.
In tricuspid atresia a hypoplastic right ventricle is present.
Tricuspid atresia frequently results in a right-to-left shunt and is linked to atrial septal defect.
Tricuspid atresia has an early cyanotic presentation.
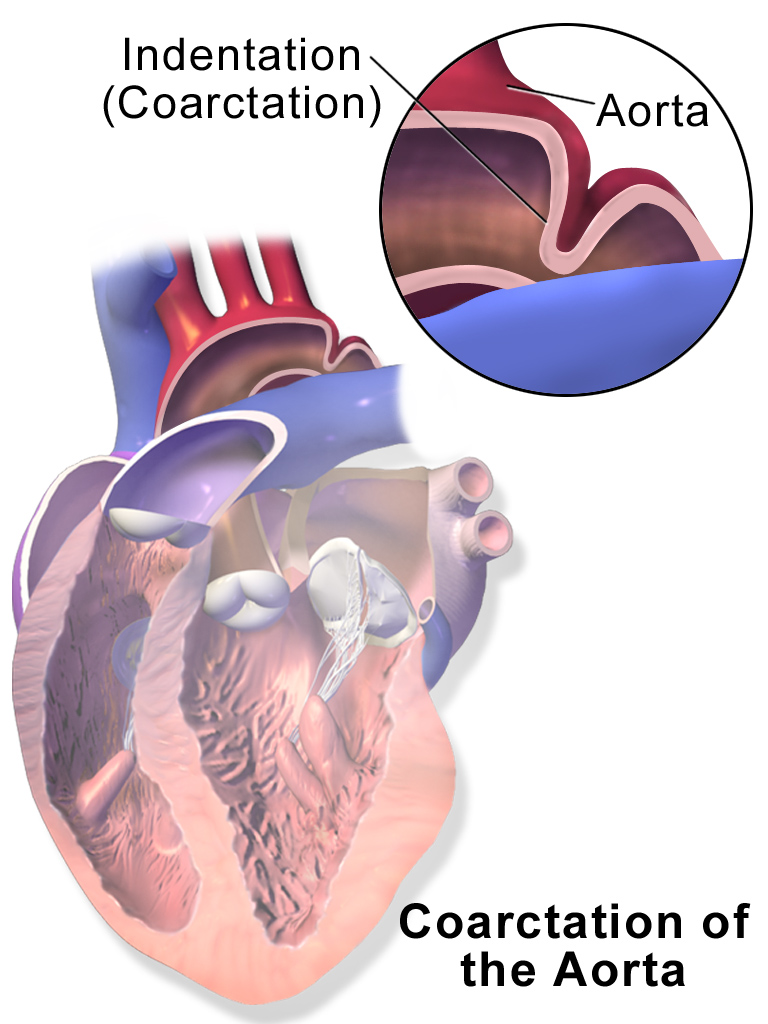
Coarctation of the Aorta
Coarctation of the aorta results in an abnormal narrowed portion of the aorta.
Coarctation of the aorta is separated into juvenile and adult versions.
Juvenile version of coarctation of the aorta
A patent ductus arteriosus (PDA), infantile form is connected.
Coarctation is located distal (after) to the aortic arch and proximally (before) to the patent ductus arteriosus (PDA).
Coarctation of the aorta presents in babies as lower extremity cyanosis, mostly after birth.
Coarctation of the aorta is linked to Turner syndrome (monosomy X).
Adult version of coarctation of the aorta
A patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) is not connected to adult form of coartctation of the aorta.
After (distal to) the aortic arch is where the coarctation is typically located in adults.
Coarctation of the aorta in adults typically presents with:
- Hypertension in the upper extremities
- Hypotension with weak pulses in the lower limbs
Radiology of coarctation of the aorta classically shows “notched ribs” on an x-ray due to collateral vessels.
Coarctation of the aorta is linked with the bicuspid aortic valve.