For macroscopic descriptions of skin lesions:
- Blister: A a vesicle or bulla.
- Bulla: A fluid-filled raised lesion greater than 5 mm across.
- Excoriation: A traumatic lesion characterized by breakage of the epidermis, leading to a raw linear area often self-induced.
- Lichenification: Prominent skin markings as a result of repeated rubbing in susceptible persons, the skin is thickened and rough.
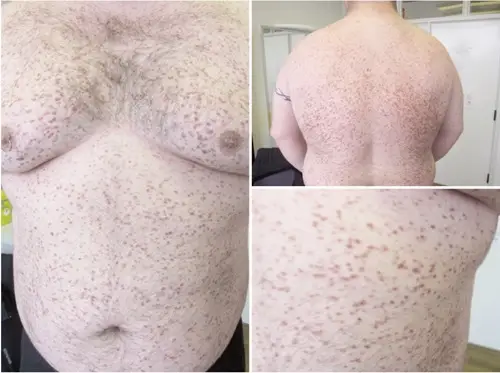
- Macule: Flatness and usually distinguished from surrounding skin by its coloration circumscribed lesion of up to 5 mm in diameter.
- Nodule: A raised lesion with a spherical contour greater than 5 mm across.
- Onycholysis: Parting of the nail plate from the nail bed.
- Patch: A circumscribed lesion of more than 5 mm in diameter considered by its evenness and usually illustrious from surrounding skin by its coloring.
- Papule: Raised flat-topped or dome-shaped lesion measuring 5 mm or less across.
- Plaque: Elevated, greater than 5 mm across and flat-topped lesion.
- Pustule: A separate, pus-filled, elevated lesion.
- Scale: A result of imperfect cornification characterized by dry, horny, platelike excrescence.
- Vesicle: A fluid-filled raised lesion 5 mm or less across.
For microscopic descriptions of skin lesions:
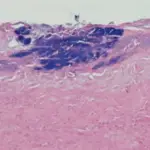
- Acanthosis: A diffuse epidermal hyperplasia.
- Dyskeratosis: An atypical keratinization happening prematurely within individual cells or groups of cells below the stratum granulosum.
- Erosion: The discontinuity to the skin showing incomplete loss of the epidermis.
- Exocytosis: The penetration of the epidermis by inflammatory or circulating blood cells.
- Hydropic Swelling: Intracellular edema of keratinocytes, frequently in viral contagions.
- Hypergranulosis: Stratum granulosum hyperplasia, frequently due to concentrated rubbing.
- Hyperkeratosis: Stratum corneum thickening, linked to a qualitative abnormality of the keratin.
- Lentiginous: A linear pattern of melanocyte proliferation within the epidermal basal cell layer.
- Papillomatosis: The surface raise triggered by hyperplasia and amplification of contiguous dermal papillae.
- Parakeratosis: The means of keratinization branded by the retaining of the nuclei in the stratum corneum, normal on mucous membranes.
- Spongiosus: The intercellular edema of the epidermis.
- Ulceration: The discontinuity of the skin unveiling complete loss of the epidermis and frequently of portions of the dermis and subcutaneous fat.
- Vacuolization: The development of vacuoles in or next to cells, usually referring to the basal cell-basement membrane zone area.