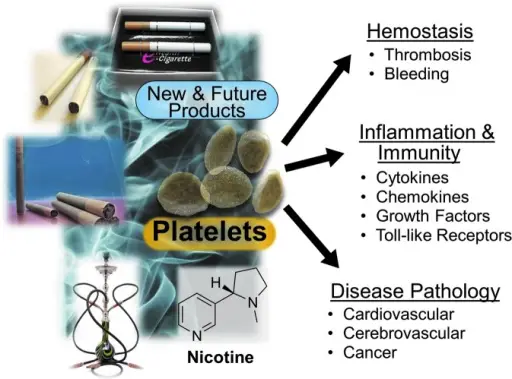
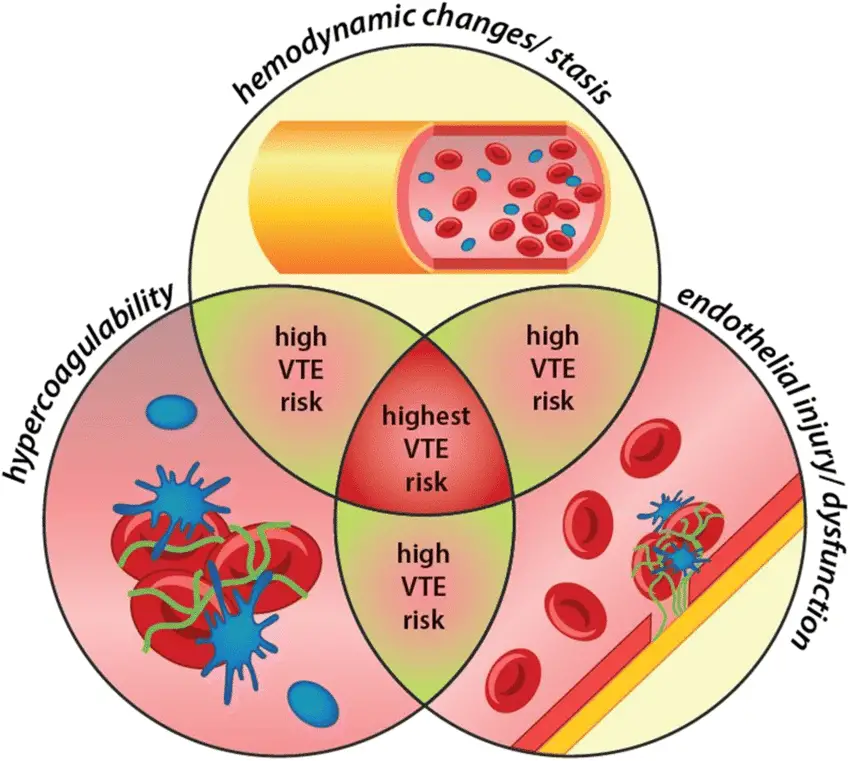
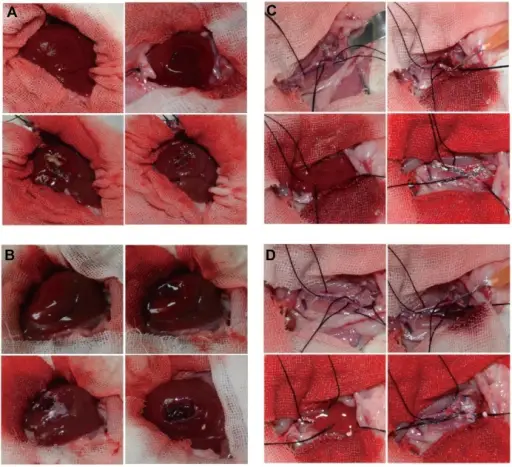
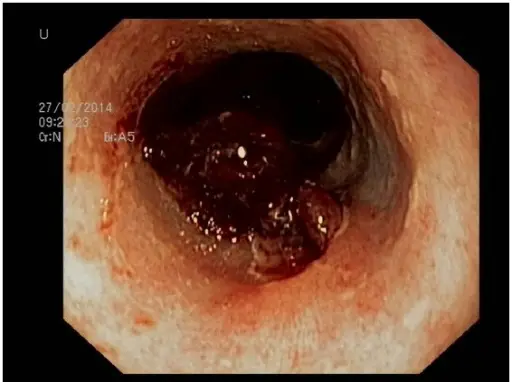
Secondary Hemostasis Pathology Study Guide
Secondary Hemostasis Secondary Hemostasis Pathology Video The whole point of secondary hemostasis is to stabilize the platelet plug. The main end product of the coagulation cascade is thrombin. Secondary hemostasis utilizes the coagulation cascade to stabilize the frail platelet plug.…