Abnormalities of placental Implantation are the large group of disorders that are associated with significant maternal, fetal, and neonatal morbidity such as placenta previa, placenta accrete, vasa previa, and velamentous cord insertion.
What is the Pathology of Abnormalities of Placental Implantation?
The pathology of abnormalities of placental implantation is:
-Etiology: The cause of abnormalities of placental implantation is blood flow problems.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to abnormalities of placental implantation shows decreased or absent decidualized endometrium resulting in abnormal implantation and increased placental adhesion.
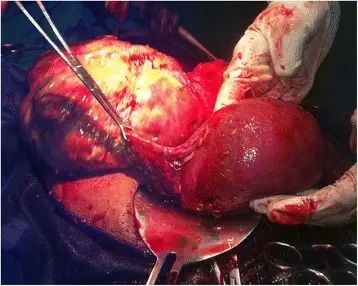
-Morphology: The morphology associated with abnormalities of placental implantation shows low-lying placenta, velamentous cord insertion, and fetal vessels that may be near or over the cervical os.
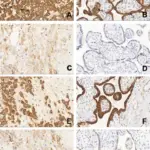
-Histology: The histology associated with abnormalities of placental implantation shows basal chronic villitis, chronic lymphoplasmacytic inflammation in the basal plate, and villous agglutination. Retromembranous hemorrhage, subchorionic intervillous thrombi, and chorionic villi extending into myometrial vascular spaces may also be present.
How does Abnormalities of Placental Implantation Present?
Patients with abnormalities of placental implantation are pregnant females. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with abnormalities of placental implantation include placental bulge with the distorted uterine outline, uterine serosal hypervascularity, and vaginal bleeding.
How is Abnormalities of Placental Implantation Diagnosed?
Abnormalities of placental implantation are diagnosed by doing an ultrasound during the second trimester.
How is Abnormalities of Placental Implantation Treated?
Abnormalities of placental implantation are treated using the medication, pelvic rest, and activity restrictions.
What is the Prognosis of Abnormalities of Placental Implantation?
The prognosis of abnormalities of placental implantation is poor with increased mortality rate.