Adrenal cysts are rare cystic masses that arise from the adrenal gland.
What is the Pathology of Adrenal Cysts?
The pathology of adrenal cysts is:
-Etiology: The cause of adrenal cysts is unknown, but risk factors for adrenal tumors can include Carney complex, Li-Fraumeni syndrome, multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2, and neurofibromatosis type 1.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to adrenal cysts is that the basic cell of origin of the cyst can be an endothelial cell lining lymphatic channels. The primary and secondary cystic malignancies and cases of cysts due to parasites should be classified separately from the adrenal cysts of lymph endothelial origin which probably represent a benign tumor-like overgrowth.
-Morphology: The morphology associated with adrenal cysts shows small: < 3 cm, round, or ovoid homogeneous lesions with smooth borders.
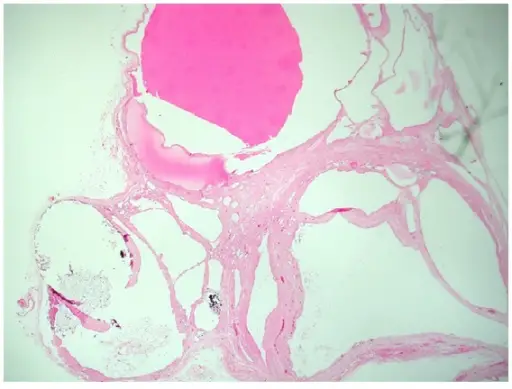
-Histology: The histology associated with adrenal cysts shows pseudocysts to malignant cystic neoplasms.
How does Adrenal Cysts Present?
Patients with adrenal cysts typically are either male or female present at the age range of all age groups. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with adrenal cysts include high blood pressure, low potassium level, heart palpitations, nervousness, feelings of anxiety or panic attacks, headache, heavy sweating/perspiration, and diabetes.
How are Adrenal Cysts Diagnosed?
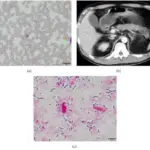
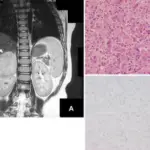
Adrenal cysts are diagnosed with imaging studies, such as computed tomography (CT) scanning of the adrenals, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and ultrasonographic examination.
How are Adrenal Cysts Treated?
Adrenal cysts are treated with laparoscopic adrenalectomy.
What is the Prognosis of Adrenal Cysts?
The prognosis of adrenal cysts is fair.