Astrocytomas originate in a particular kind of glial cells, star-shaped brain cells in the cerebrum called astrocytes.
What is the Pathology of Astrocytomas?
Etiology: The cause of Astrocytomas is not known. Genetic and immunologic abnormalities, environmental factors, diet, stress, and/or other factors may play contributing roles in causing specific types of cancer.
Genes involved: Astrocytomas can have a genetic link when they are associated with a few rare, inherited disorders. These include neurofibromatosis type I, Li-Fraumeni syndrome, Turcot syndrome, and tuberous sclerosis.
Pathogenesis: The exact pathogenesis of astrocytoma is not completely understood but it is believed that this tumor has a close association with genetic mutations. The origin of this tumor is from neuroepithelial cells.
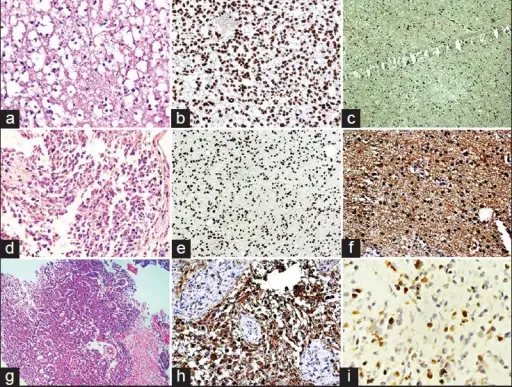
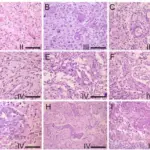
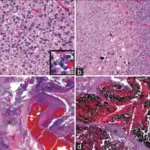
Histology: The histology associated with Astrocytomas shows diffuse astrocytomas with a mild increase in cellularity and fibrillary background.
How does Astrocytoma Present?
Patients with Astrocytomas typically are older males. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with Astrocytomas include headaches, vision changes, seizures, and fatigue.
How is Astrocytoma Diagnosed?
Astrocytomas are diagnosed through clinical evaluation, characteristic physical findings, a careful patient history, and specialized tests, such as blood tests, neuroimaging techniques, and a biopsy.
How is Astrocytoma Treated?
Astrocytomas are treated by surgical resection with or without chemotherapy.
What is the Prognosis of Astrocytoma?
The prognosis of Astrocytoma fair.