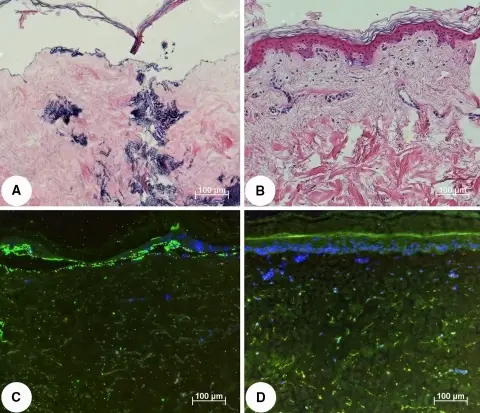
H&E staining of infected skin (a) and non-infected control (b) at day 7 after S. aureus infection. Inoculated tissue presents with epidermolysis and bacterial infection in comparison to a regularly structured epidermis in the control. Lower panel immunohistochemical staining of infected (c) and non-infected (d) skin with anti-S. aureus antibody (green) and DAPI counterstaining (nucleus, blue). A novel human skin chamber model to study wound infection ex vivo: Steinstraesser L, Sorkin M, Niederbichler AD, Becerikli M, Stupka J, Daigeler A, Kesting MR, Stricker I, Jacobsen F, Schulte M - Archives of dermatological research (2009). Not altered. CC.
Bacterial Infections occur when bacteria enter the body, increase in number, and cause a reaction in the body.
Bacterial Infections include:
- Gram-positive bacterial infections
- Gram-negative bacterial infections
- Mycobacteria bacterial infections
- Spirochete bacterial infections
- Anaerobic bacterial infections
- Obligate intracellular bacterial infections