Capillary hemangiomas are the most common type of benign tumors composed of blood-filled vessels, mostly on the skin, subcutaneous tissues, oral cavities mucous membranes.
What is the Pathology of Capillary Hemangiomas?
The pathology of capillary hemangiomas is:
-Etiology: The cause of capillary hemangiomas is hamartomatous proliferations
-Genes involved: Unknown.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to capillary hemangiomas, thought to result from vascular endothelial cells hamartomatous propagations.
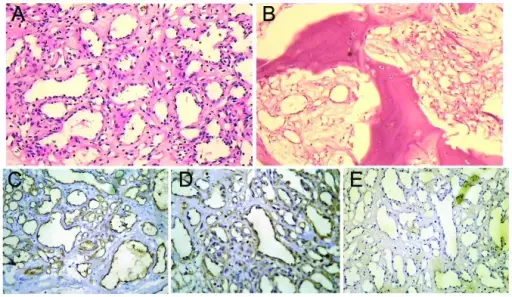
-Morphology: The morphology associated with capillary hemangiomas shows varying in size, bright red to blue, and slightly raised lesion.
-Histology: The histology associated with capillary hemangiomas shows lobulated, unencapsulated aggregates, and flattened endothelium.
How does Capillary Hemangiomas Present?
Patients with capillary hemangiomas are typically females more than males that are young. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with capillary hemangiomas include red spot growing, ptosis eyelid.
How is Capillary Hemangiomas Diagnosed?
Capillary hemangiomas is diagnosed through laboratory studies such as positive factor VIII immunohistochemical staining. Imaging studies include ultrasonography indicates irregular lesion contour, CT scan, and MRI.
How is Capillary Hemangiomas Treated?
Capillary hemangiomas is treated through medical care such as corticosteroid therapy, propranolol therapy, interferon alfa therapy, and timolol therapy. Surgical care may also be useful.
What is the Prognosis of Capillary Hemangiomas?
The prognosis of capillary hemangiomas is good. Lesions may resolve on there own.