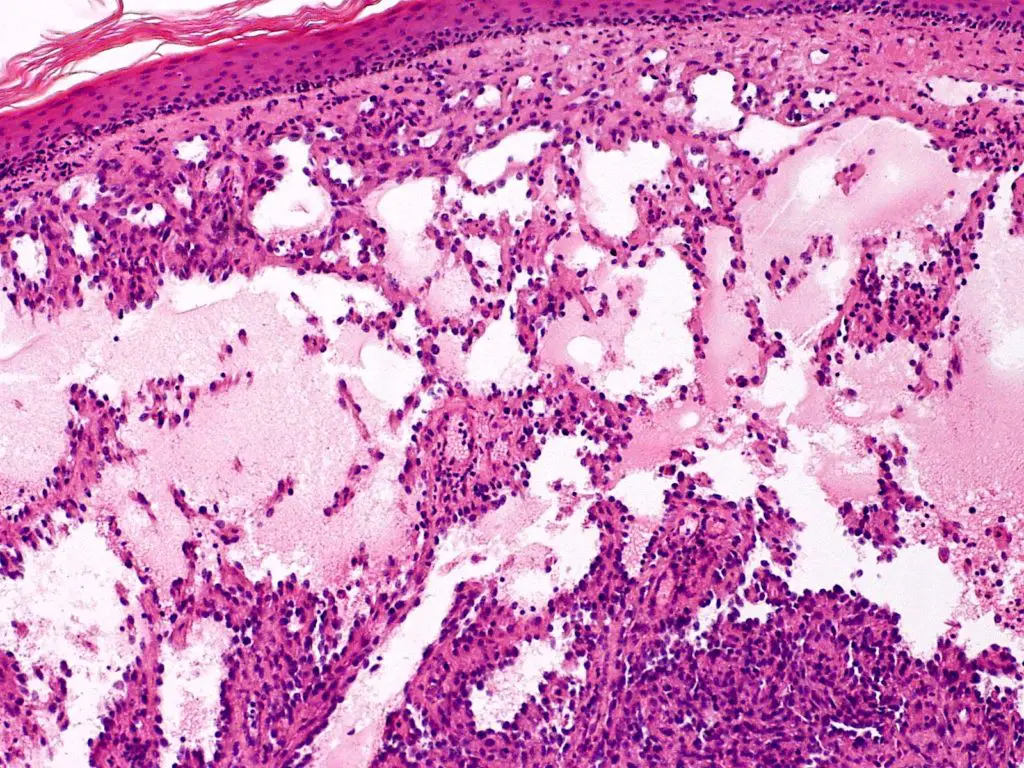
Capillary lymphangiomas are also known as simple lymphangiomas, and are composed of small, lymphatic vessels located at the epidermis.
What is the Pathology of Capillary Lymphangiomas?
The pathology of capillary lymphangiomas is:
-Etiology: The cause of capillary lymphangiomas is an idiopathic associated lymphatic blockage.
-Genes involved: Unknown.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to capillary lymphangiomas is not clearly understood.
-Morphology: The morphology associated with capillary lymphangiomas shows a little raised or sometimes pedunculated lesions up to 1 to 2 cm in diameter that occur predominantly in the head, neck, and axillary subcutaneous tissues.
-Histology: The histology associated with capillary lymphangiomas shows acanthosis and hyperkeratosis.
How do Capillary Lymphangiomas Present?
Patients with capillary lymphangiomas typically have no sex predilection, and present at an age range of infancy to 5 years old. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with capillary lymphangiomas include trivial clusters of blisters on the skin prone to bleeding.
How are Capillary Lymphangiomas Diagnosed?
Capillary lymphangiomas are diagnosed through imaging studies which include ultrasound, MRI, CT scan, and biopsy.
How is Capillary Lymphangiomas Treated?
Capillary lymphangiomas are treated through medical care. Surgical excision may also be beneficial.
What is the Prognosis of Capillary Lymphangiomas?
The prognosis of capillary lymphangiomas is good with proper complete surgical excision.