Cavernous hemangiomas are benign tumors composed of blood-filled vessels that are more infiltrative, often involving deep structures.
What is the Pathology of Cavernous Hemangiomas?
The pathology of cavernous hemangiomas is:
-Etiology: Unknown.
-Genes involved: Unknown.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to cavernous hemangiomas, thought to result from vascular endothelial cells hamartomatous propagations.
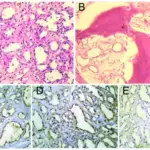
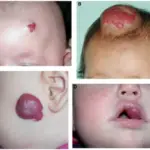
-Morphology: The morphology associated with cavernous hemangiomas shows a red-blue, soft, spongy mass 1 to 2 cm in diameter.
-Histology: The histology associated with cavernous hemangiomas shows unencapsulated, large cavernous blood-filled vascular spaces separated by connective tissue stroma.
How does Cavernous Hemangiomas Present?
Patients with cavernous hemangiomas are more commonly in females that present at an age range of 30 to 40 years old. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with cavernous hemangiomas include painless, slowly advancing protrusion. Change of visual acuity in case of eye involvement, and diplopia.
How is Cavernous Hemangiomas Diagnosed?
Cavernous hemangiomas is diagnosed through imaging studies such as CT scan, and ultrasound.
How is Cavernous Hemangiomas Treated?
Cavernous hemangiomas is treated through surgical care for cosmetic purposes.
What is the Prognosis of Cavernous Hemangiomas?
The prognosis of cavernous hemangiomas is good. Most require no intervention.