Cavernous lymphangiomas are types of lymhangiomas that are classically found on the neck, and axilla.
What is the Pathology of Cavernous Lymphangiomas?
The pathology of cavernous lymphangiomas is:
-Etiology: The cause of cavernous lymphangiomas is idiopathic associated lymphatic blockage.
-Genes involved: Unknown.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to cavernous lymphangiomas not clearly understood, results from lymphatic system blockage during fetus deployments.
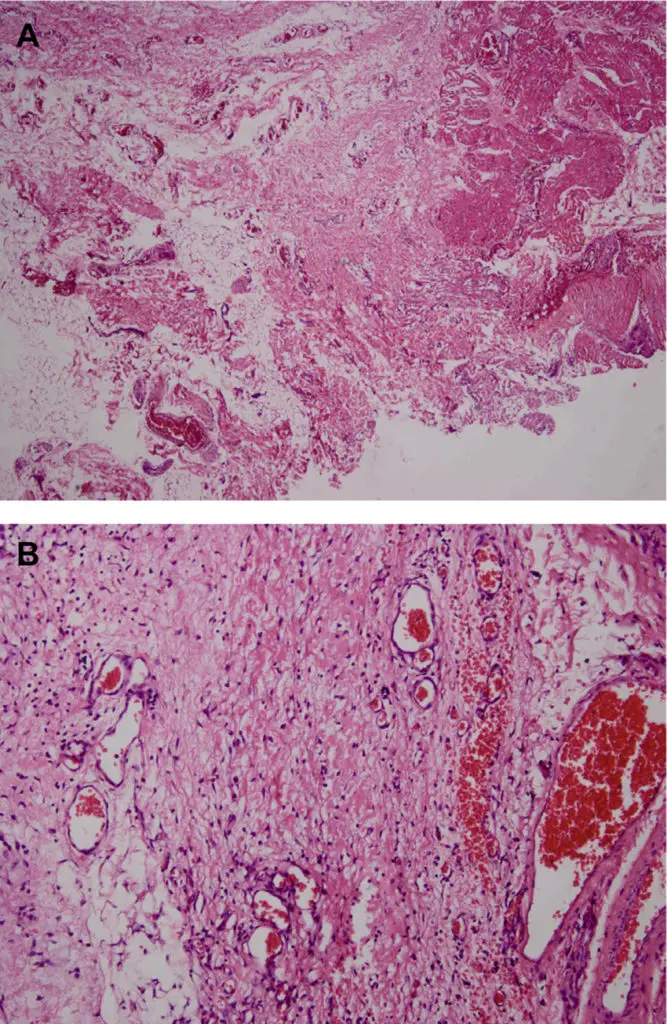
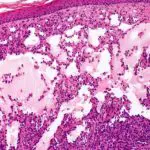
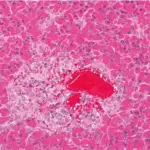
-Morphology: The morphology associated with cavernous lymphangiomas shows dilated lymphatics.
-Histology: The histology associated with cavernous lymphangiomas shows enormously dilated lymphatic spaces lined by endothelial cells.
How do Cavernous Lymphangiomas Present?
Patients with cavernous lymphangiomas typically have no sex predilection and present at an age range of infancy to 5 years old. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with cavernous lymphangiomas include rubbery subcutaneous nodules.
How are Cavernous Lymphangiomas Diagnosed?
Cavernous lymphangiomas is diagnosed through imaging studies such as ultrasound, MRI, and CT scan. Biopsy may also be useful.
How is Cavernous Lymphangiomas Treated?
Cavernous lymphangiomas is treated through surgical excision.
What is the Prognosis of Cavernous Lymphangiomas?
The prognosis of cavernous lymphangiomas is good with proper management.