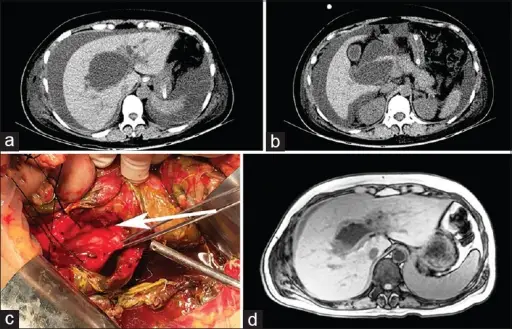
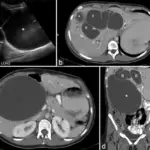
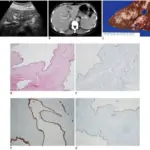
Choledochal cysts are rare congenital dilations that carry bile from the liver to the small intestine for digestion.
What is the Pathology of Choledochal Cysts?
The pathology of choledochal cysts is:
-Etiology: The cause of choledochal cysts is the abnormal intersection between the bile duct and pancreatic duct.
-Genes involved: Unknown.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to choledochal cysts includes defects in epithelialization and recanalization of the developing bile ducts and congenital weakness of the ductal wall.
-Histology: The histology associated with choledochal cysts shows focal columnar epithelium, walls composed of dense fibrous tissue, scattered smooth muscle, and elastic fibers.
How does Choledochal Cysts Present?
Patients with choledochal cysts typically affect children (girls) and are usually congenital. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with choledochal cysts include abdominal mass, pain in the right upper belly, jaundice, nausea and vomiting.
How is Choledochal Cysts Diagnosed?
Choledochal cysts is diagnosed using ultrasound, CT scan, and cholangiography.
How is Choledochal Cysts Treated?
Choledochal cysts is treated with bile duct surgery with total cyst removal.
What is the Prognosis of Choledochal Cysts?
The prognosis of choledochal cysts is good with early total resection and reconstruction.