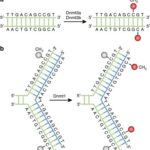
Chromatin organizing factors: histone chaperones, histone modifying enzymes and ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling complexes.
What are Chromatin Organizing Factors?
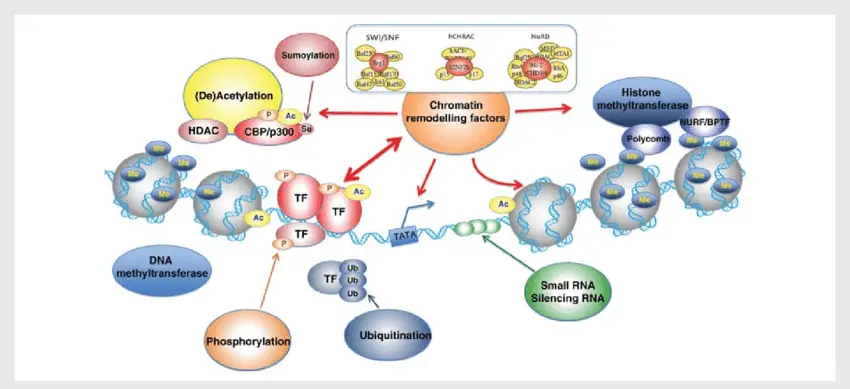
Chromatin structure and remodelling factors. DNA is organized in chromatin composed of condensed nucleosomes: units of 146 bp of DNA wrapped twice around an octamer of two copies of each histone protein H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. The flexible amino-terminal tails of the histones, protruding outward from the nucleosome, allow for post-translational modifications through (de)acethylation, phosporylation, ubiquitination, methylation, and sumoylation. Such covalent modifications alter DNA-histone interactions, affecting accessibility of transcription factors. Not altered. CC.
Epigenetic factors and cardiac development
Jan Hendrick van Weerd, Kazuko Koshiba-Takeuchi, Chulan Kwoz,and Jun K. Takeuchi