| Disease | Genetic Issue | Clinical Features |
| Klinefelter syndrome | X extra chromosome | Infertility and small, poorly functioning testicles. |
| Pure gonadal dysgenesis | None. | Impaired development of the gonads. |
| XYY male | Extra Y chromosome (47XYY) | Taller than average height, low muscle tone, or muscle weakness, clinodactyly, widely spaced eyes, behavioral disorders. |
| XXX female | Extra X chromosome (47XXX) | Learning disabilities, mild dysmorphic features such as hypertelorism and clinodactyly, early menopause, and increased height. |
| Mixed gonadal dysgenesis | 45,XO/46,XY mosaicism | Asymmetry in gonadal development of testis and streak gonad. |
| Turner syndrome | Completely missing second X chromosome (45,X or 45,X0) | Short stature, streak ovary, shield chest, bicuspid aortic valve, coarctation of the aorta, lymphatic defects (result in webbed neck or cystic hygroma; lymphedema in feet, hands), horseshoe kidney, high-arched palate, shortened 4th metacarpals. |
What Are Chromosomal Disorders?
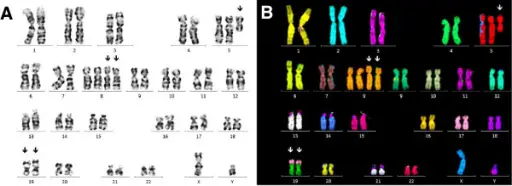
GTG-banded karyotype and multicolor-FISH image at second relapse. (A) The predominant aberrant subclone 1 shows gain of i(5)(p10), tetrasomy 8 and two derivative chromosomes 19. (B) Multicolor-FISH analysis confirmed the chromosomal aberrations and unveiled the unbalanced der(19)t(17;19). Arrows point to chromosomal abnormalities. A case of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with an unreported combination of chromosomal abnormalities: gain of isochromosome 5p, tetrasomy 8 and unbalanced translocation der(19)t(17;19)(q23;p13). Paar C, Herber G, Voskova D, Fridrik M, Stekel H, Berg J - Molecular cytogenetics (2013). Not Altered. CC.