Complex multigenic disorders include:
- Normal karyotype
- Structural abnormalities of chromosomes
- Chromosomal disorders
- Trisomies
- Trisome 21
- Trisomy 18
- Trisomy 13
- Trisomy 22
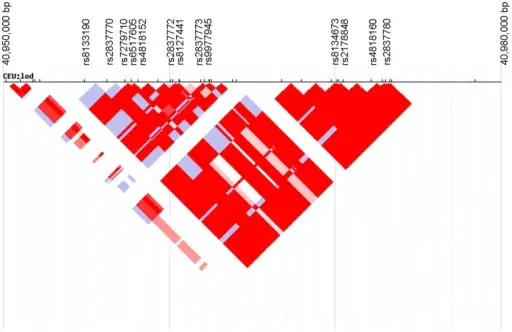
| Disease | Clinical Features |
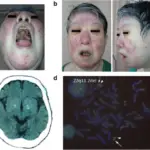
| Down syndrome (trisomy 21) | Intellectual disability, prominent epicanthal folds, single palmar crease, flat facies, incurved 5th finger, gap between 1st 2 toes, duodenal atresia, Hirschsprung disease, congenital heart disease (atrial septal defect), and brushfield spots. Associated with early-onset Alzheimer disease (chromosome 21 codes for amyloid precursor protein), increase risk of AML/ALL. |
| Edwards syndrome (trisomy 18) | Prominent occiput, rocker-bottom feet, intellectual disability, clenched fists, overlapping fingers, low-set ears, micrognathia (small jaw), congenital heart disease, omphalocele, myelomeningocele. Death usually occurs by 1 year of age. |
| Patau syndrome (trisomy 13) | Intellectual disability, rocker-bottom feet, microphthalmia, microcephaly, cleft lip/palate, holoprosencephaly, polydactyly, cutis aplasia, congenital heart disease, polycystic kidney disease, omphalocele. Death usually occurs by 1 year of age. |
| Schmid–Fraccaro syndrome (trisomy 22) | Abnormalities of the eyes, ears, anal region, heart and/or kidney. |