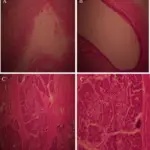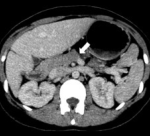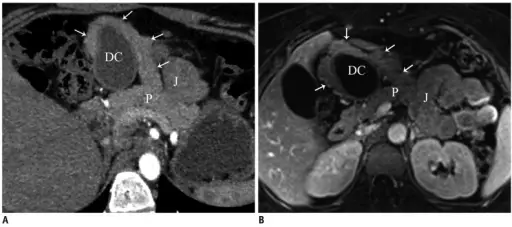
Accessory pancreatic lobe.Oblique axial (A) and fat suppressed contrast-enhanced T1-weighted gradient echo (B) MR images show accessory pancreatic lobe (arrows) that has similar attenuation and signal intensity to pancreatic tissue (P), arising from pancreas, projecting anteriorly and attaching to gastric duplication cyst (DC). P = pancreas, J = jejunum. Congenital variants and anomalies of the pancreas and pancreatic duct: imaging by magnetic resonance cholangiopancreaticography and multidetector computed tomography. Türkvatan A, Erden A, Türkoğlu MA, Yener Ö - Korean journal of radiology (2013). Not Altered. CC.
Congenital anomalies of the pancreas are the abnormal functions and structure of the pancreas that develop during the complex process by which the dorsal and ventral pancreatic primordia fuse during pancreatic development.
Examples of congenital anomalies of the pancreas include:
- Agenesis of the pancreas
- Annular pancreas
- Ectopic pancreas
- Pancreas divisum