Corneal degenerations are the gradual degeneration of the cornea tissue.
What are Corneal Degenerations?
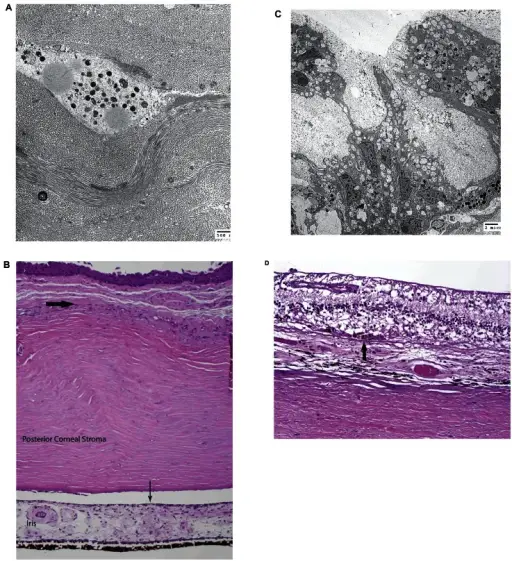
Transmission electron micrograph of ocular tissues with late BCDA) and B) Cornea. A) Electron micrograph of the corneal stroma. Corneal degeneration is present as irregularly banded collagen fibers and calcium deposition consistent with scar. There is no evidence of lysosomal crystals in the cornea at this stage. B) Light micrograph of the peripheral cornea. Bowman’s membrane is absent and has been replaced by degenerative fibrous pannus (thick arrow). The anterior contour of the iris is flattened due to the presence of iris neovascularization. (hematoxylin-eosin stain, original magnification × 40). C) and D) Retina. C) Electron micrograph of the retina. Retinal degeneration is characterized by intracellular pigmented granules and vacuolated cytoplasm. The retina and choroid also show no evidence of lysosomal crystals. D) Light micrograph of the posterior retina. There is near total degeneration of all functional elements of the retina leaving only structural astrocytes. Only a small number of recognizable retinal pigment epithelial cells remain (arrow). (hematoxylin-eosin, original magnification × 200).Evolution of Cellular Inclusions in Bietti's Crystalline Dystrophy.
Furusato E, Cameron JD, Chan CC - Ophthalmology and eye diseases (2010). Not Altered. CC