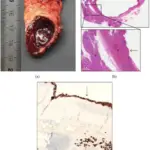
Cysts of the spleen include primary and secondary cysts, based on the existence of cellular or fibrous lining. True cysts are grouped into non-parasitic and parasitic. True non-parasitic cysts comprise congenital (epithelial), and neoplastic cysts (lymphangioma, metastases, haemangioma). False cysts may develop due to trauma, infarction-degeneration, hemorrhage, and also inflammation.
What are Cysts of the Spleen?
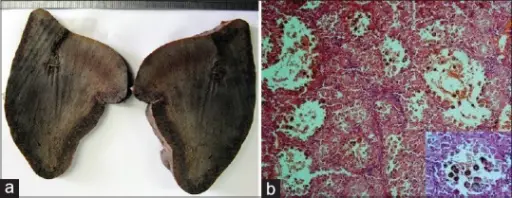
Cysts of the Spleen. (a) Cut section of spleen shows ill-defined, irregular-shaped, dark-red spongy lesion. (b) Anastomosing vascular channels with cyst like spaces filled by many sloughed endothelial cells and RBCs. (H and E ×100). Inset: Tumoral cells with intracytoplasmic hemosiderin pigment. (H and E ×400). Littoral cell angioma of the spleen: Cytological findings and review of the literature. Journal of Cytology. Not Altered. CC.