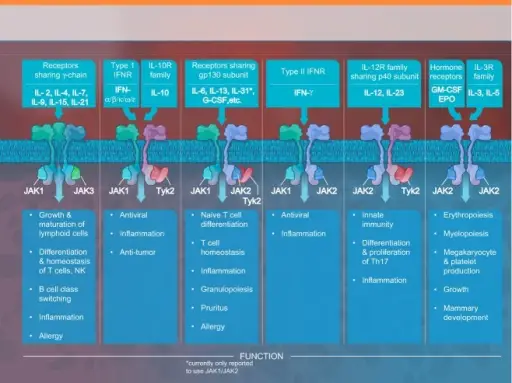
Cytokines are small proteins that are crucial in controlling the growth and activity of other immune system cells and blood cells.
| No. | Cytokines | Source | Target | Biological role |
| 1 | IL-1(IL-1α and -β) | Macrophages, dendritic cells, endothelial cells | TH and B cells and various other tissues | Activation |
| 2 | IL-2 | TH1 cells | TH, Tc and NK cells | T cell and NK proliferation and induction of activity |
| 3 | IL-3 | TH, Tc and NK cells | Hematopoietic and mast cells | Progenitor cell proliferation and differentiation |
| 4 | IL-4 | TH2 cells, mast cells, NK cells | B cells, T cells, mast cells, macrophages | Proliferation, isotype switching, induction of MHC class II expression |
| 5 | IL-5 | TH2 cells, mast cells | Eosinophils | Proliferation and differentiation |
| 6 | IL-6 | Macrophages, TH2 cells | Plasma cells, B cells and others | Differentiation and antibody secretion |
| 7 | IL-8 | Bone marrow, thymus | Neutrophils | Chemoattractant |
| 8 | IL-9 | TH2 cells | TH cells, mast cells, eosinophils | Induces inflammatory responses |
| 9 | IL-10 | TH2 cells | Macrophages, APC | Anti-inflammatory cytokine inhibits cytokine production |
| 10 | IL-11 | Bone marrow | B-cell progenitors and others | Differentiation |
| 11 | IL-12 | Macrophages, B cells | Tc, NK and LAK cells | Proliferation and differentiation in synergy with IL-2 |
| 12 | IL-13 | TH cells | Macrophages, B cells | Inhibition of inflammatory cytokines, regulation of inflammation. Parasitic infections |
| 13 | IL-16 | Tc cells | TH cells | Chemotaxis |
| 14 | 1L-18 | Hematopoietic and nonhematopoietic lineage cells | T cells, NK cells | Proinflammatory cytokine; IFN-γ inducing factor |
| 15 | IFN-α | Leukocytes | Inhibitor of viral replication | |
| 16 | IFN-β | Fibroblasts | Inhibitor of viral replication | |
| 17 | IFN-γ | TH1, TC, NK | Various cells including macrophages | Inhibitor of viral replication, Inhibitor of cell proliferation. Inhibitor of IL-4 induced isotype switching |
| 18 | TNF-α | Macrophages | Tumour cells, polymorphonuclear leukocytes, macrophages | Cytotoxicity, induction of cytokine secretion |
| 19 | TNF-β | T cells | Tumour cells, neutrophils, macrophages | Cytotoxicity, phagocytosis |