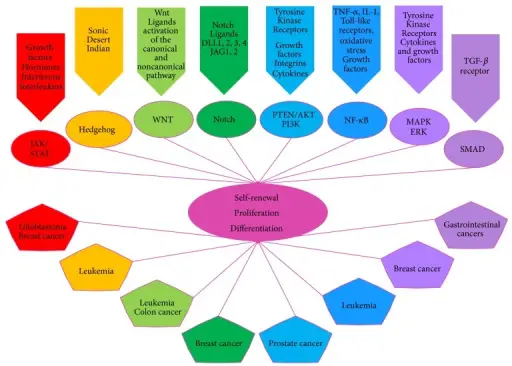
Common signaling pathways between Stem Cells (SCs) and Cancer Stem Cells (CSCs) [48]. CSCs share common signaling pathways, like the JAK/STAT, Hedgehog, Wnt, Notch, PTEN/AKT/P13K, NF-κB, MAPK/ERK, and SMAD. These SCs mechanisms are altered in CSCs and are characteristic of the cancer types mentioned. The JAK/STAT pathway (Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription) is mainly involved in glioblastoma development and breast CSCs [49–52]. The Hedgehog pathways have effects on the patterning of the embryo but play a crucial role in the induction of myelogenous leukemia. Blocking of the Hedgehog pathway decreases the quantity of CSCs in leukemia, then representing an important target for cancer therapy [53]. The Wnt pathway is an important regulator of SCs and CSCs regarding self-renewal, being perturbed in colon cancer and leukemia [54–56]. The Notch pathway is involved in the development of breast tissue as a regulator of cell fate and differentiation. An excess in the activation of Notch could determine the aggressiveness of breast cancer [55, 57–59]. The phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN)/protein kinase B (PKB or AKT)/phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase (P13K) signaling is a key regulator of self-renewal and maintenance of SCs and CSCs with an important role in the emergence of CSCs in prostate cancer [51, 60]. The NF-κB pathway is crucial for leukemic cells survival and its inhibition affects CSCs development in breast cancer [61]. It has been seen that the increase of neural stem cell (NSC) proliferation is caused by the activation of NF-κB, through the TNF-α signal transduction pathway, but its aberrant regulation could lead to CSCs development in glioblastomas [62, 63]. Blocking the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) results in the growth inhibition of breast cancer and the emergence of CSCs, sensitizing cancer cells to chemotherapy [64–66]. Gastrointestinal SCs can be perturbed, changing their plasticity and differentiation potential by generating an aberrant response to TGF-β affecting the SMAD pathway and generating CSCs [67]. The hepatocellular carcinoma is an aggressive form of cancer in which the TGF-β, Notch, and Wnt are deregulated, also having consequences in the SMAD proteins and changing SCs renewal, differentiation, and survival patterns [68, 69]. In adult and CSCs systems all the mentioned pathways are common and conserved in the control of SCs renewal, proliferation, and differentiation.Stemness in Cancer: Stem Cells, Cancer Stem Cells, and Their Microenvironment
Stem Cells International. Not Altered. CC
Developmental disorders of the breast are breast issues that are due to syndromic, genetic, acquired, or sporadic conditions. Developmental disorders of the breast typically present in childhood or adolescents, but the age of presentation may vary. The clinical presentation depends on the underlying cause. Developmental disorders of the breast may be bilateral or unilateral.
Examples of developmental disorders of the breast include:
- Accessory axillary breast tissue
- Congenital nipple inversion
- Milk line remnants