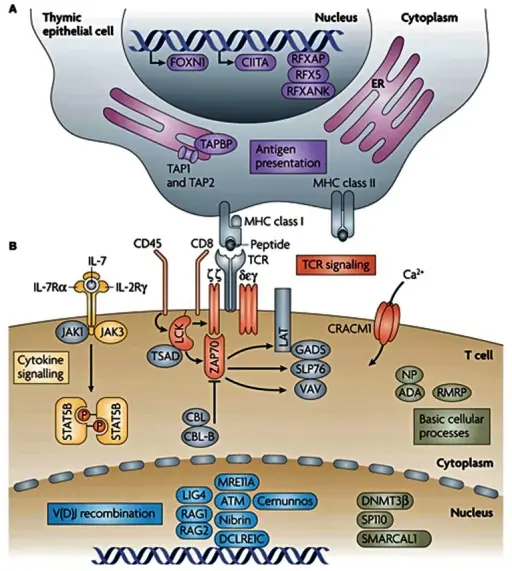
Genes with mutations that cause monogenic, severe T-cell immunodeficiency in humans can be intrinsic to the thymic epithelium or to T cells. (A) Genetic defects that are intrinsic to thymic epithelial cells ultimately affect the antigen-presentation pathway. (B) Genetic defects that are intrinsic to T cells include those that affect T-cell receptor (TCR) signaling, cytokine signaling, somatic recombination, or basic cellular processes. Other genes that are important to these pathways or processes, but have not been linked to severe T-cell deficiency in humans are shown in grey. Copyright © 2008. Nature Publishing Group. Adapted with permission from Liston A, Enders A, Siggs OM. Unravelling the association of partial T-cell immunodeficiency and immune dysregulation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8:546.80Abbreviations: ADA, adenosine deaminase; ATM, ataxia-telangiectasia mutated; CBL, Casitas B-lineage lymphoma; CIITA, class II transactivator; DCLRE1C, DNA crosslink repair 1C; DNMT3β, DNA cytosine-5 methyltransferase 3β; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; FOXN1, forkhead box N1; GADS, GRB2-related adaptor protein; IL-2RΓ, IL-2 receptor Γ-chain; IL-7, interleukin-7; IL-7Rα, IL-7 receptor α-chain; JAK, Janus kinase; LAT, linker for activation of T cells; LIG4, ligase IV; MRE11A, meiotic recombination 11 homolog A; Nibrin, Nijmegen breakage syndrome 1; NP, nucleoside phosphorylase; CRACM1, calcium release-activated calcium modulator 1; RAG, recombination-activating gene; RFX5, regulatory factor X5; RFXANK, RFX-associated ankyrin-containing protein; RFXAP, RFX-associated protein; RMRP, RNA component of mitochondrial RNA-processing endoribonuclease; SLP76, SRC-homology-2-domain-containing leukocyte protein of 76 kDa; SMARCAL1, SWI/SNF-related matrix-associated actin-dependent regulator of chromatin a-like 1; SP110, SP110 nuclear body protein; STAT5B, signal transducer and activator of transcription 5B; TAP, transporter associated with antigen processing; TAPBP, TAP-binding protein; TSAD, T-cell-specific adaptor protein; ZAP70, ζ-chain-associated protein kinase of 70 kDa. The genetic basis of severe combined immunodeficiency and its variants. Tasher D, Dalal I - The application of clinical genetics (2012). Not Altered. CC.
Disorders associated with defects in receptor proteins are structural abnormalities of receptor proteins, that altered their function of receiving and transducing signals.
An example is familial hypercholesterolemia.
